Docket #: S18-188
Biodegradable and Flexible Arterial Pulse Sensors for the Wireless Monitoring of Blood Flow
Stanford researchers at the Zhenan Bao Lab have designed a device and method for real-time monitoring of arterial blood flow using a biodegradable, flexible, wireless and battery-free sensor mounted on an artery. Monitoring blood flow after vascular anastomosis (surgically connecting blood vessels) is critical to patient recovery and patient outcomes after complex reconstructive surgeries.
This sensor can be operated wirelessly through inductive coupling, has minimal hysteresis, fast response times, excellent cycling stability, is highly robust, and eliminates the need for removal, thus reducing the risk of vessel trauma. A prototype was successfully tested with a custom-made artificial artery model and in vivo in rats. The team believes this is the first demonstration of a wireless, biodegradable sensor that can monitor blood flow in an artery in real-time.
Stanford News Article: January 8, 2019
"Stanford researchers create a wireless, battery-free, biodegradable blood flow sensor"
Figure
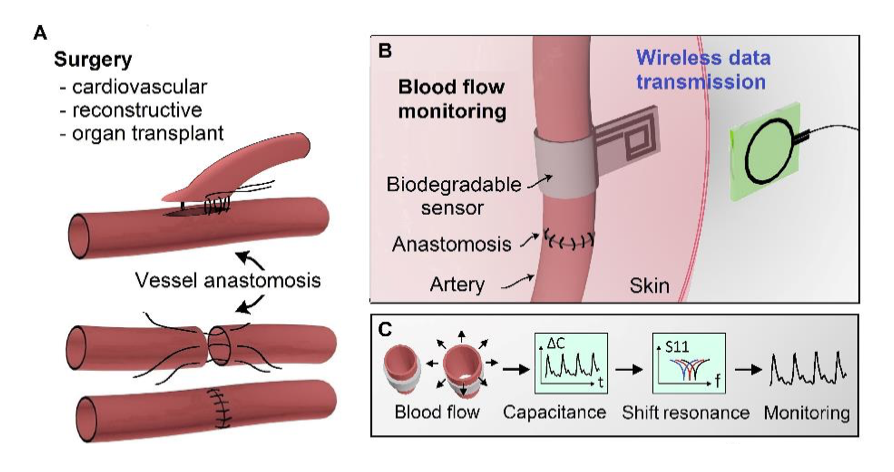 Figure description - Biodegradable, flexible and passive arterial-pulse sensor design
Figure description - Biodegradable, flexible and passive arterial-pulse sensor design
Stage of Research
Applications
- Post-operative monitoring of blood flow after surgical procedures that require vessel anastomosis, which include cardiac, vascular, transplant and reconstructive operations
Advantages
- Biodegradable sensor with biocompatible materials, thus eliminates need for removal
- Real time, continuous blood flow monitoring post-surgery
- Wireless and battery-free
- Simple fabrication process
- Two operating modes:
- Can measure the blood flow both in contact (pressure sensing) and
- non-contact (fringe-field sensing) modes
- Can replace other costly, complex and wired methods such as
- External Doppler evaluation
- Visual assessment of skin color and turgor
- Wired implantable Doppler system
- Cuff-type Hall-effect sensor for pulse-monitoring
- Color duplex sonography
- Near infrared spectroscopy
Publications
- Boutry, Clementine M., Levent Beker, Yukitoshi Kaizawa, Christopher Vassos, Helen Tran, Allison C. Hinckley, Raphael Pfattner et al. "Biodegradable and flexible arterial-pulse sensor for the wireless monitoring of blood flow." Nature Biomedical Engineering 3, no. 1 (2019): 47.
Related Links
Similar Technologies
-
Self-Powered Electronic Skin S14-211Self-Powered Electronic Skin
-
Passive Miniature Wireless Pressure Sensor for Bio-monitoring S13-130Passive Miniature Wireless Pressure Sensor for Bio-monitoring
-
Highly Stretchable and Tough Self-healing Elastomer for Electronic Skin S17-032Highly Stretchable and Tough Self-healing Elastomer for Electronic Skin