Docket #: S17-441
BodyNET: Sensor System for wearable electronics
Stanford researchers at the Bao Research Group have patented a body area sensor network (bodyNET) that can be used to monitor human physiological signals for next-generation personalized healthcare. BodyNET is composed of chip-free and battery-free stretchable on-skin sensor tags that are wirelessly linked to flexible readout circuits attached to textiles.
Graphical Abstract
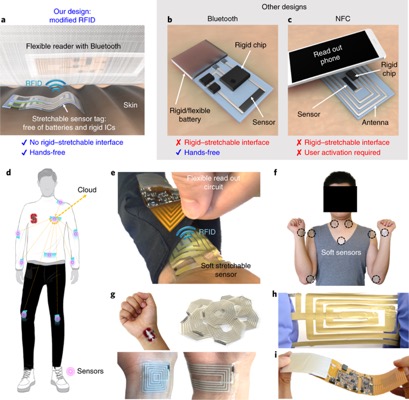
Figure description - a Schematic to describe a sensor node that thoroughly eliminates the interconnect between rigid and soft components. A stretchable sensor is conformably attached on skin and collects the signals. The information is wirelessly read out by a flexible printed circuit board (FPCB) initiator on clothing. b,c, Schematics for conventional Bluetooth (b) and NFC (c) designs that have been developed previously for wearable sensors. d, Design concept of the bodyNET. e, Photograph of one sensor node for sensing the pulse on a human wrist. f, Photo of a person wearing multiple skin sensors. g, Photograph of on-skin sensors with different designs. h, Photo of a stretched target. i Photo of a bent FPCB initiator.
Image credit: Bao Research Group
Stage of Development
Stanford News Article,
"Stanford engineers have developed wireless sensors that stick to the skin to track our health" August 16, 2019
Related Technologies
Stanford Docket S19-292 "Stretchable multi-sensor tag for wearable electronics"
Stanford Docket S19-032 "Coupling Insensitive compact reader for fully-passive sensors"
Applications
- Wearable electronics for health monitoring or other skin sensing
- Internet-of-things (IoT)
Advantages
- Batteryless, chipless and wireless on-skin sensor tag for wearable electronics
- Low power requirements
- Uses novel RFID/NFC technology
- Receiver and transmitter can be close together
- Can operate on multiple frequencies
- Platform has many possible variations
- Novel features:
- First intrinsic stretchable NFC wireless sensor tag on skin
- First intrinsic NFC stretchable antenna
- First intrinsic stretchable nF level capacitor
- First hybrid design of flexible circuit board and intrinsic stretchable tag
Publications
- Niu, Simiao, Naoji Matsuhisa, Levent Beker, Jinxing Li, Sihong Wang, Jiechen Wang, Yuanwen Jiang et al. "A wireless body area sensor network based on stretchable passive tags." Nature Electronics (2019): 1-8.
Related Links
Patents
- Issued: 10,635,868 (USA)
Similar Technologies
-
Coupling Insensitive compact reader for fully-passive sensors S19-032Coupling Insensitive compact reader for fully-passive sensors
-
Stretchable multi-sensor tag for wearable electronics S19-292Stretchable multi-sensor tag for wearable electronics
-
A biomimetic electronic skin (e-skin) with discriminating forces S18-419A biomimetic electronic skin (e-skin) with discriminating forces