Docket #: S22-308
Composite Inclusion Graft for Ross Procedure
Stanford researchers at the Woo Lab have invented a composite inclusion graft that addresses several challenges associated with the Ross procedure, such as late autograft dilation.
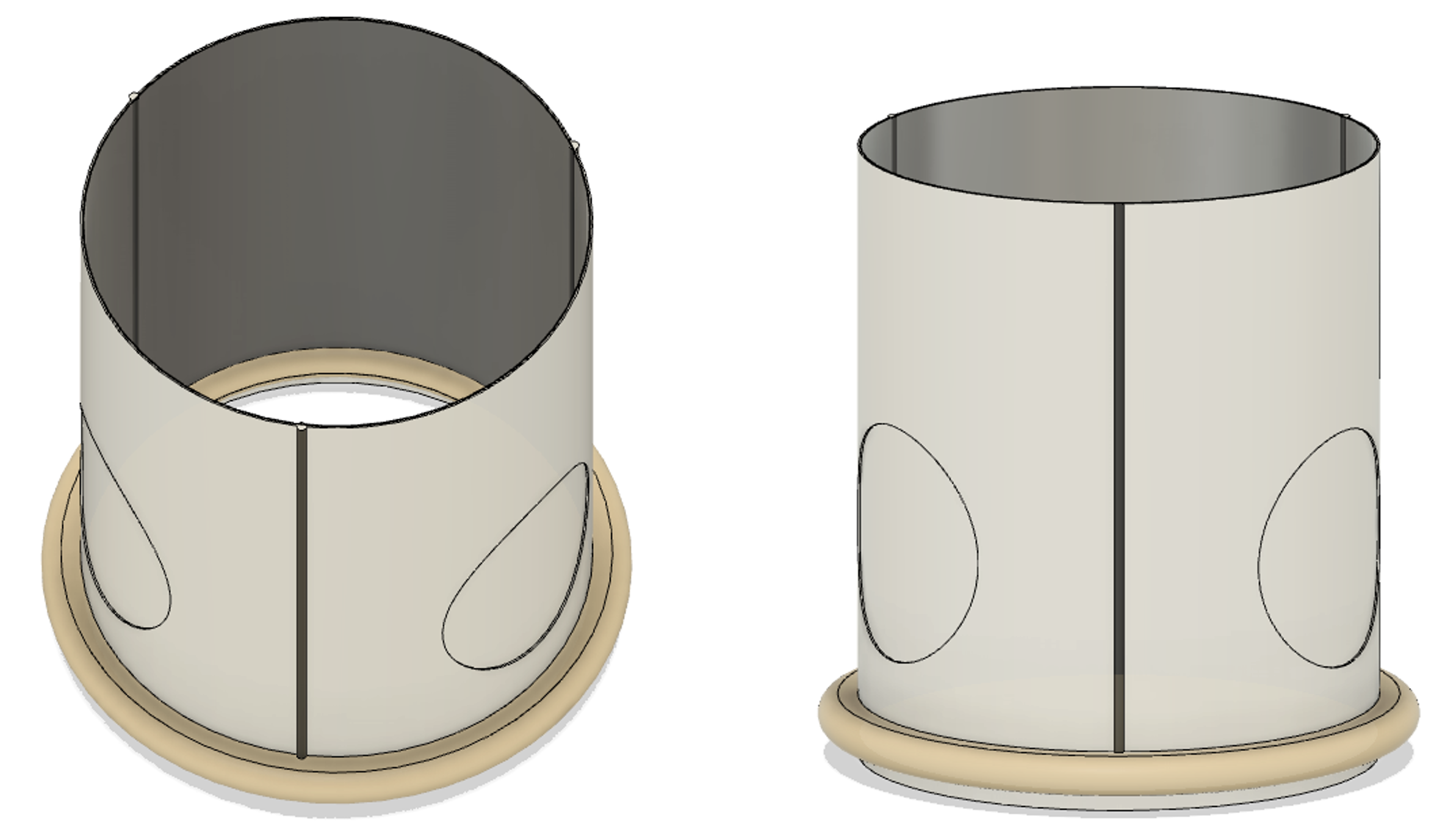
The device consists of a straight Dacron graft with a rigid sewing ring for autograft proximal anastomosis, and it includes reference markings for precise commissure suspension. To accommodate different surgical preferences, circular markings on the graft can be utilized for direct anastomosis or left intact for a 3-layered anastomosis. The inclusion technique aims to support the autograft and prevent late dilation but may be challenging to perform. Surgeons face potential issues such as distorted neo-annulus during autograft implantation and bleeding complications during coronary button anastomosis, especially with the 3-layered technique, which may result in pressure build-up and potential blood flow occlusion.
This change to the inclusion technique was developed to support the autograft and prevent this late autograft dilation. The change to this composite graft is very intuitive-to-use, easy-to-incorporate, prevents neo-annulus distortion in the aortic root, and allows for different options for coronary button anastomosis.
Stage of Development
Prototype Design
Figure
Related Technologies
Stanford docket S22-333 "Geometric Aortic Graft" describes an advanced version of conventional aortic grafts with a reinforced suture area which reduces bleeding around the anastomosis line.
Stanford docket S22-404 "Innovative prosthetic valve design for severe mitral annular calcification" describes an innovative prosthetic valve which ensures a perfect seal to eliminate risk of potential para-valvular leaks.
Applications
- Ross Procedure for aortic valve replacement
Advantages
- Very intuitive to use
- Easy to incorporate
- Prevents neo-annulus distortion in the aortic root
- Allows for different options for coronary button anastomosis
Related Links
Similar Technologies
-
Innovative prosthetic valve design for severe mitral annular calcification S22-404Innovative prosthetic valve design for severe mitral annular calcification
-
Geometric Aortic Graft S22-333Geometric Aortic Graft
-
Compact, optical sensor device to measure forces on mitral valve structures prior to surgical repair or replacement S18-298Compact, optical sensor device to measure forces on mitral valve structures prior to surgical repair or replacement