Docket #: S17-416
Frequency-based multiplexing technique for high density recording of electrodes
Stanford researchers have designed a frequency-multiplexed neural probe architecture that enables massive scaling of electrophysiological recording from neurons.
Multiplexing of many electrodes for brain neuron sensing is extremely difficult due to the requirement of using very little physical space. An array of "oscillatrodes" (oscillator-under-electrodes) are distributed along a probe and the outputs are coupled and transmitted using a single wire to overcome the space limitation. One application is for brain machine interface (BMI) to help paralysis patients regain functionality for improved quality of life.
A 65-nm CMOS prototype including eight ring oscillators has been implemented for study and characterization.
Figure:
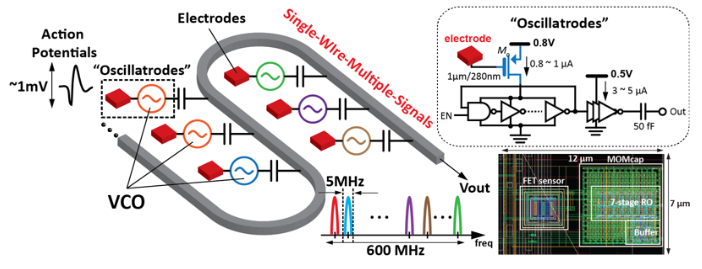
Figure Description: Frequency-multiplexed neural probe using oscillatrodes.
Stage of Development:
Applications
- Brain Machine Interface (BMI) - neural probes on brain cortex, surface electrodes on brain cortex
- Therapeutic applications:
- Neurodegenerative diseases
- Spinal cord injuries
- Clinical research
- Other applications include but are not limited to: retina implant, cell-based assay for drug screening, Internet-of-Things (IoT), CMOS imager, 2D ultrasound transducer, MRI coil array detection, DNA microarrays, DNA sequencing arrays, high-energy physics experiments, and Large-scale IoT wireless sensor networks
Advantages
- High-throughput simultaneous recording at massive scale
- Multiplexed onto a single wire overcoming space limitations
- High spatial and temporal resolution
- Other techniques cannot achieve all of the following five performance metrics simultaneously: (1) high pixel density (2) reduced number in the interconnect counts (3) reduced shank width in neural probe platform (4) miniaturized implant size (5) scalable wireless connectivity
Publications
- IEEE EMBC NER Conference 2019 9th International IEEE/EMBS Conference on Neural Engineering (NER) March 20-23, 2019, San Francisco, CA, USA, Paper FrPO.190 "A Study of Frequency-Multiplexed "Oscillatrodes" for Ultra-High-Density Neural Probes"
Related Links
Patents
- Published Application: WO2020124030
Similar Technologies
-
Neural device implantation for electrical stimulation of neural/biological tissue S18-050Neural device implantation for electrical stimulation of neural/biological tissue
-
Passive Miniature Wireless Pressure Sensor for Bio-monitoring S13-130Passive Miniature Wireless Pressure Sensor for Bio-monitoring
-
Ultrasound for Detecting and Suppressing Epileptic Seizure S18-336Ultrasound for Detecting and Suppressing Epileptic Seizure