Docket #: S20-203
Multifocal macroscope for large field of view imaging of dynamic specimens
Researchers at Stanford have developed a technique that leverages multifocal widefield optics to enable high-speed, synchronous, genetically-specified recording of neural activity across the entirety of mouse dorsal cortex at near-cellular resolution. The technique, called COSMOS, has one primary component: a one-photon multifocal macroscope with large field of view, high light collection, high sampling rate, and good image quality that is compatible with fluorescent specimens. Current approaches are powerful but limited by speed or resolution; COSMOS leverages existing technology in new ways to enable advanced performance. The primary application is basic brain science research, and it may also be useful for pharmaceutical development or as a more general, low-cost means of tracking the movement or dynamics of particles in 3-D space. Currently, no comparable method exists for simultaneously measuring neuronal activity dynamics at or near cellular resolution across 3-D, centimeter-scale fields of view at video-rate speeds.
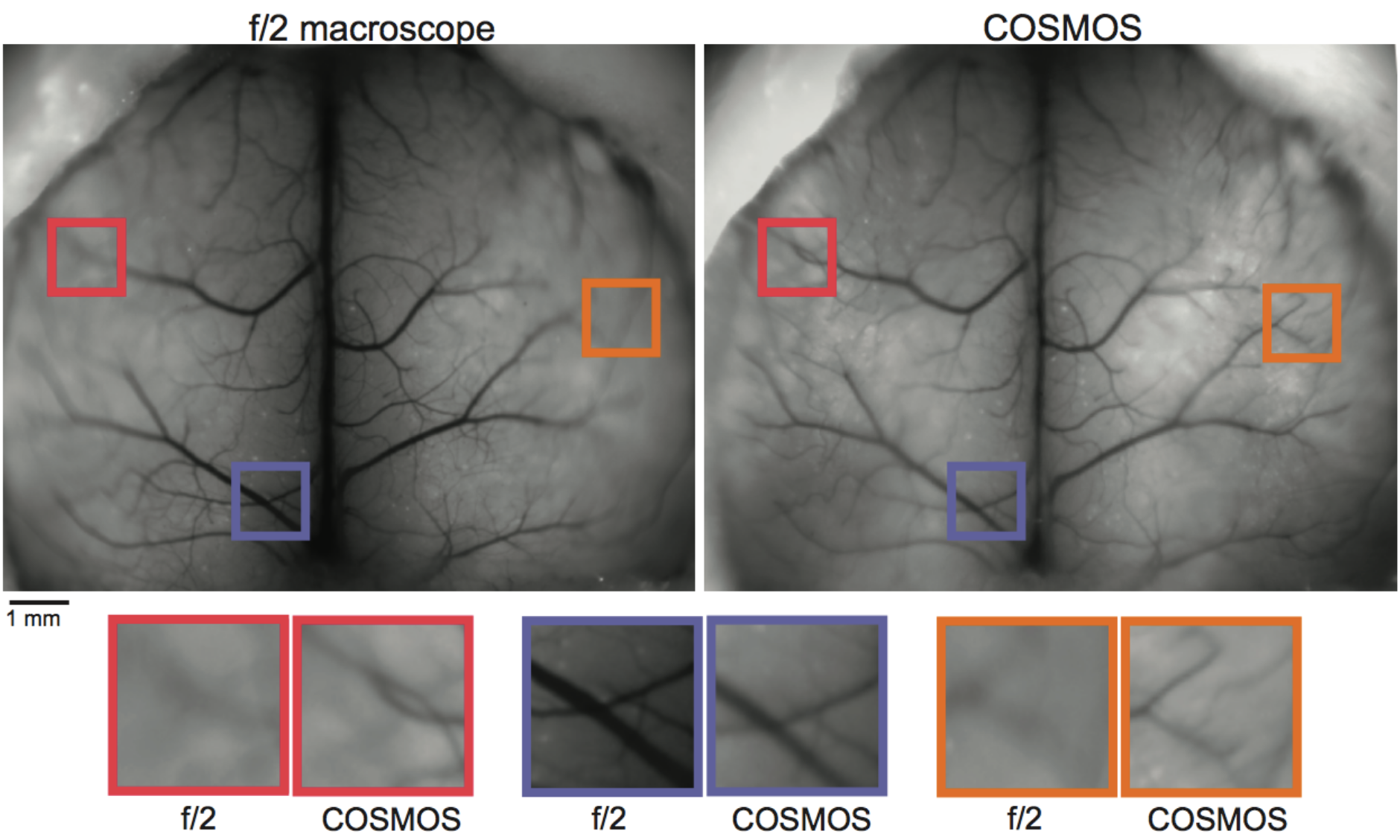
Merged image quality vs. a conventional macroscope with the same light throughput. COSMOS yields high quality extended depth of field. (image credit: the inventors)
Stage of Development
COSMOS allowed simultaneous recording of neural dynamics at ~30 Hz from over a thousand near-cellular resolution neuronal sources spread across the entire dorsal neocortex of awake, behaving mice during a three-option lick-to-target task. Initial experiments illustrate how COSMOS enables investigation of large-scale cortical dynamics.
Applications
- Non-invasive, chronic neural activity recording in rodents
- Imaging particle motion
- Brain machine interfaces/neural decoding
- Monitoring neural activity during rodent testing of novel psychopharmaceuticals
- Monitoring blood flow in rodent testing of models for stroke/cortical infarction
- In vivo imaging of tumor growth
- Functional imaging of stem cells growth/organoids
Advantages
- 1cm x 1cm x 1.2mm field of view
- Video rate (~30 Hz) speed
- Single camera operation
- Cost effective and easy to assemble
- Demonstrated application to neural decoding
Publications
- Isaac V. Kauvar, Timothy A. Machado, Elle Yuen, John Kochalka, Minseung Choi, William E. Allen, Gordon Wetzstein, Karl Deisseroth, Cortical Observation by Synchronous Multifocal Optical Sampling Reveals Widespread Population Encoding of Actions, Neuron, 107 (2), 2020, 351-367.e19, ISSN 0896-6273 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2020.04.023.
Patents
- Published Application: 20210364771
- Issued: 11,912,271 (USA)
Similar Technologies
-
RNA fixation and detection in CLARITY-based hydrogel tissue S15-424RNA fixation and detection in CLARITY-based hydrogel tissue
-
3D Super Resolution Microscopy with a Bisected Phase Mask: A Device to Measure the Depth, Position and Orientation of Single Molecules S13-4923D Super Resolution Microscopy with a Bisected Phase Mask: A Device to Measure the Depth, Position and Orientation of Single Molecules
-
Ultrafast Multifocal Multiphoton Microscope S13-139Ultrafast Multifocal Multiphoton Microscope