Docket #: S22-239
A Tunable, Nanophotonic Metamaterial 'Super Scintillator' for PET Imaging
Stanford scientists have invented a new PET-nanophotonic metamaterial scintillator that consists of tunable scintillating alkaline-earth rare-earth fluoride nanoparticles (MLnF) for low-dose, high-resolution PET imaging.
Scintillators, used in PET imaging, are materials that convert high-energy radiation into low-energy photons in the UV-Vis region. An ultrafast scintillator can largely improve the coincidence timing window (CTR) and allow for better signal localization. Current state-of-the-art scintillators have decay constants of 200ns-1000ns. Although there are some scintillators like BaF2 which have ultrafast decay constants, they are impractical due to low radiative efficiency. To address this challenge, the inventors have successfully designed and optimized fabrication of tunable, purcell enhanced metamaterial scintillators made of alkaline rare-earth fluoride nanoparticles with decay times of 10ps. Inventors also developed a novel nanoparticle self-assembly fabrication method in which scintillating nanoparticles can be 3D printed in lieu of expensive monocrystal growth and labor-intensive physical fabrication methods to create metamaterial scintillating detectors.
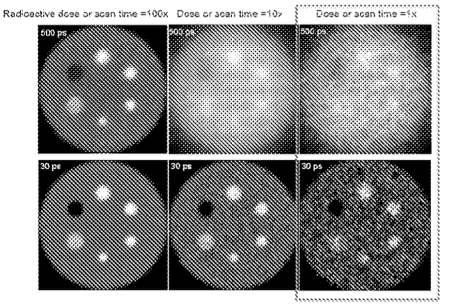
Figure Description: This figure shows example image quality gains from improved coincidence time resolution from 500ps to 30ps TOF-PET. (Image Credit: Inventors)
Stage of Development
Proof of Concept
Applications
- High resolution clinical PET for diagnosis of cancer, cardiovascular and neurological disorders
Advantages
- Improved coincidence time resolution (CTR) due to:
- Increased light yield
- Short decay time
- Increased PET image signal-to-noise ratio (SNR)
- Tunable to optimize for broad spectral range
- Cost-efficient and scalable synthesis method
- Lower injected radiation dose, hence safer
- Shorter scan duration
Related Links
Similar Technologies
-
Methods and Systems for increasing the sensitivity of simultaneous multi-isotope positron emission tomography S11-011Methods and Systems for increasing the sensitivity of simultaneous multi-isotope positron emission tomography
-
PET tracers for imaging bacterial infection S13-084PET tracers for imaging bacterial infection
-
Novel PET imaging agents for the detection of CA6 epitope in-vivo S12-506Novel PET imaging agents for the detection of CA6 epitope in-vivo