Docket #: S16-007
ATAC-see: a method for integrated imaging and sequencing of the accessible genome
Researchers at Stanford University have developed ATAC-see (Assay of Transposase-Accessible Chromatin with visualization), a one-step strategy to image and sequence regulatory DNA. Eukaryotic genomes are generally compacted into chromatin except for the active regulatory elements that control gene activity. The spatial organization of these accessible elements is linked to gene expression, replication and DNA repair, however the in situ organization is largely unknown. To overcome this, the inventors have developed the ATAC-see method. It uses a novel bifunctional enzyme complex. When the complex is placed on cell samples it simultaneously makes the active regulatory DNA fluorescent and ready for sequencing. This method enables direct imaging of the accessible genome in situ, cell sorting, and deep sequencing to reveal the identity of the imaged elements. ATAC-see provides a combination of spatial and epigenomic information for a molecular portrait of the cell.
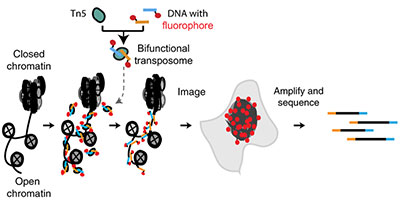
Stage of research
The ATAC-see method has been used to examine the spatial organization of the accessible genome in its native context for a variety of cell types, including five human cell types.
Applications
- Research:
- Single cell analysis
- Morphological identification of diseased cells
- Prospective sorting of cells based on regulatory DNA status
- Identification of regulatory DNA by imaging and sequencing
Advantages
- New method to:
- Capture spatial information on regulatory DNA in intact cell
- Sort cells based on status of regulatory DNA
- Image and sequence DNA from the same sample
- Allows identification of epigenomic information from formalin-fixed cells, including clinical samples
- Integrated preassembled system that performs imaging and sequence library preparation at the same time
- Easy quality control for DNA sequencing libraries
- Labeling strategy is compatible with different fluorophores and chemical tags compatible with multimodal imaging of landmark proteins
Publications
- Chen X, Shen Y, Draper W, Buenrostro JD, Litzenburger U, Cho SW, Satpathy AT, Carter AC, Ghosh RP, East-Seletsky A, Doudna JA, Greenleaf WJ, Liphardt JT, Chang HY, ATAC-see reveals the accessible genome by transposase-mediated imaging and sequencing, Nature Methods, 2016 Oct 17. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.4031.
Additional Patent Information
- Issued patent in US (see Patent section below) and pending patents in Europe, China and Singapore
Related Links
Patents
- Published Application: WO2017156336
- Published Application: 20190071656
- Published Application: 20240076637
- Issued: 11,680,253 (USA)
Similar Technologies
-
Statistical system to quantify biomolecular samples S18-060Statistical system to quantify biomolecular samples
-
STR-Seq: a technology for massively parallel STR sequencing and genotyping S15-164STR-Seq: a technology for massively parallel STR sequencing and genotyping
-
Fast, direct DNA capture and sequencing S10-233Fast, direct DNA capture and sequencing