Docket #: S22-051
CCSNet web app: a deep learning modeling suite for CO2 storage
Stanford researchers in the Benson Lab have developed CCSNet, an open source software platform for modeling CO2 storage reservoirs based on machine learning neural networks. As compared to current standards, this software is 10,000 to 100,000 times faster and more accurate.
Traditional simulators for carbon geological storage are computationally expensive and time consuming. Trained with a large numerical simulation data set, CCSNet provides numerous outputs for carbon dioxide storage projects including but not limited to CO2 gas saturation, pressure buildup, and mass balance.
Stage of Development
Figure:
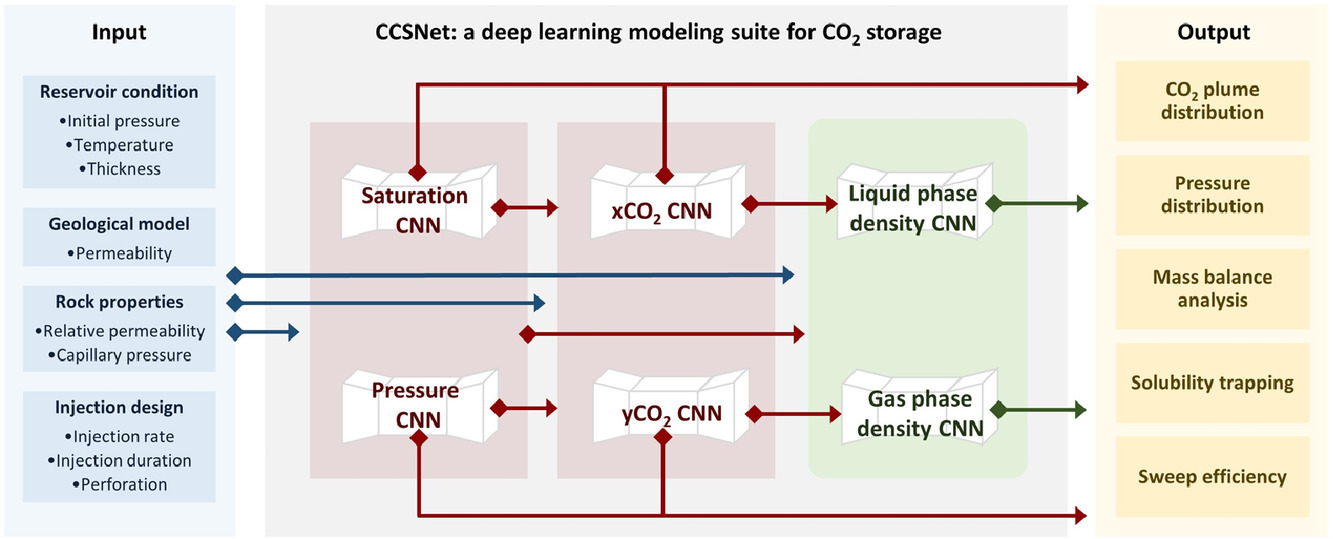
Figure description: Graphical Abstract
Image credit: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2021.104009
Applications
- Numerical simulation for carbon storage
Advantages
- Instant and accurate predictions - 10,000 to 100,000 times faster compared to competitive top tier numerical simulations
- 2D version is open source. License available for 3D and webcode.
Publications
- Wen, G., Tang, M., & Benson, S. M. (2021).Towards a predictor for CO2 plume migration using deep neural networks. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control, 105, 103223.
Related Links
Similar Technologies
-
Metal catalysts in tandem with carbon-based catalysts for CO2 conversion to carbon-based molecules S21-448Metal catalysts in tandem with carbon-based catalysts for CO2 conversion to carbon-based molecules
-
Thermal process to transform silicate minerals into alkaline solids for carbon removal S23-304Thermal process to transform silicate minerals into alkaline solids for carbon removal
-
Biomimetic Sorbents for CO2 Capture S12-500Biomimetic Sorbents for CO2 Capture