Docket #: S20-039
Enhanced activation of CD8+ and CD4+ T cells by a vaccine targeting CD244 or CD48
Researchers at Stanford have developed a microparticle-based vaccine that in a single shot enables enhanced activation of CD8+ and/or CD4+ T cells to fight against infectious diseases and cancer. Development of T cell-directed vaccines are important to prevent infectious diseases especially the chronic and persistent ones caused by complex pathogens in case of HIV and malaria. Though the challenge lies in inducing activation of CD8+ and CD4+ T cells in sufficient magnitude. Similarly, cancer immunotherapies can benefit from a robust priming of CD8+ and CD4+ T cell to achieve effective tumor killing. This vaccine platform offers a promising solution whereby a single delivery of microparticles with antibodies against receptor CD244 (2B4, SLAMF4) or CD48 (SLAMF2) can allow sufficient CD8+ and CD4+ T cells activation. Additionally, the technology has the potential to treat allergic and autoimmune diseases if administrated alone or in combination with immunosuppressive molecules.
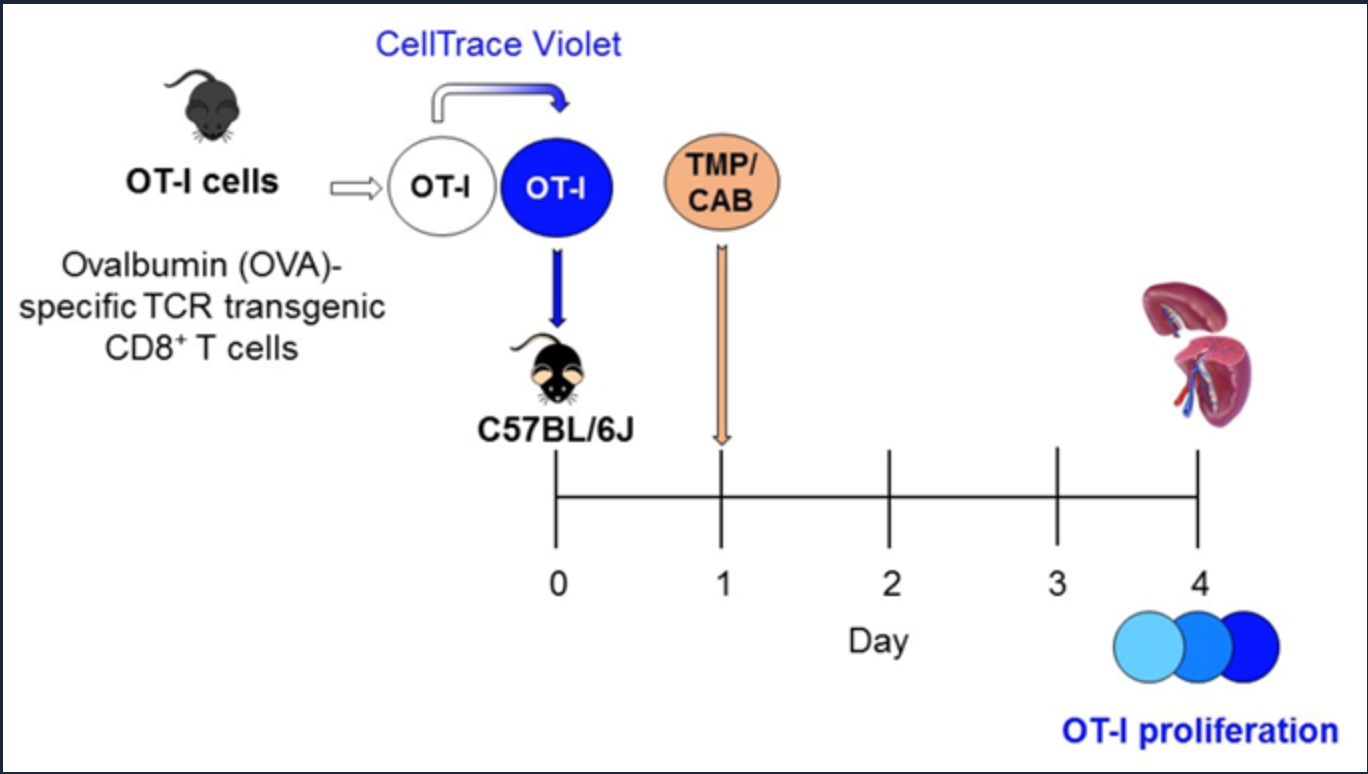
anti-CD244 targeted microparticles (TMPs) prime antigen specific CD8+ T cells in vivo
image credit: inventor
Stage of Development
Technology has been demonstrated in mice.
Applications
- Modulating T cell and antibody-mediated immune responses in cancers, infectious diseases (viral and parasitic), allergic reaction and autoimmune diseases.
Advantages
- Potential to stimulate or suppress immune response in humans
- Dual targeting of receptor and natural ligand
Patents
- Published Application: WO2021207249
- Published Application: 20230149540
Similar Technologies
-
Composition and Method for Autonomous RNA Switches for Translational Control S23-162Composition and Method for Autonomous RNA Switches for Translational Control
-
Methods to Prevent T-cell Exhaustion and Improve CAR-T Cell Immunotherapy with Small Molecules S17-119BMethods to Prevent T-cell Exhaustion and Improve CAR-T Cell Immunotherapy with Small Molecules
-
Cell-free Production of Plasmids for Genetic Medicines S24-353Cell-free Production of Plasmids for Genetic Medicines