Docket #: S24-490
Enhanced SOC Estimation for LFP Batteries: Synergistic Approach Using Coulomb Counting Reset, Machine Learning, and Relaxation
Researchers in the Onori Lab have developed a state of charge (SOC) estimation technique for Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) batteries using machine learning. LFP batteries account for over 30% of lithium battery cathode chemistries and are increasingly used for EVs and grid storage due to safety, sustainability, and cost advantages and resilience to supply chain disruptions LFP battery path-dependent behavior, hysteresis effects , and flat open circuit voltage (OCV) characteristics challenge traditional model-based SOC estimation methods that rely on OCV-SOC relationships.
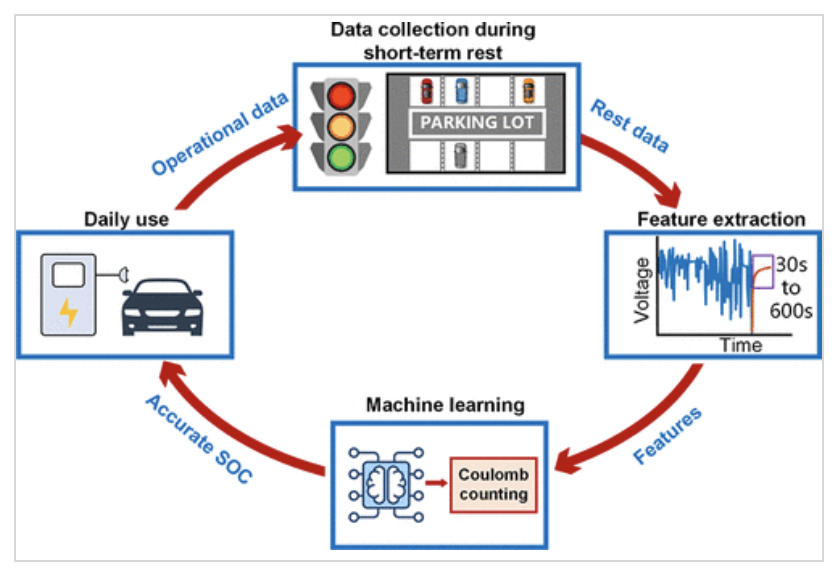
State of Charge (SOC) Estimation for Lithium-Iron Phosphate (LFP) Batteries
(Image courtesy the Onori Lab)
The Onori Lab machine learning-based SOC estimation approach:
-
Enhances the standard Coulomb counting method by addressing incorrect initialization
Uses relaxation voltage and temperature measurements during short rest periods (when current is zero)
Incorporates historical current data to improve estimation accuracy
Works with low sampling frequency data (1/30 Hz), making it practical for real-world Battery Management Systems
This solution offers practical implementation for battery management systems in electric vehicles and energy storage applications, with potential extension to state-of-health estimation.
Stage of Development – Proof of Concept
Extensive testing across 430+ working conditions demonstrated mean absolute errors below 3.25% with just one minute of relaxation voltage data. The approach is robust to various conditions and machine learning algorithms.
Applications
- LFP battery state-of-charge (SOC) estimation for:
- Electric and hybrid vehicles
- Consumer electronics
- Smart grids and Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS)
Advantages
- More accurate & computationally faster SOC estimate
- Minimal computational resources
- Seamless integration into existing BMS, uses existing sensors
- Longer, more predictable battery operation
- Potentially extendable to state-of-health estimation
Publications
- Che, Y., Xu, L., Teodorescu, R., Hu, X., & Onori, S. (2025). Enhanced SOC Estimation for LFP Batteries: A Synergistic Approach Using Coulomb Counting Reset, Machine Learning, and Relaxation. ACS Energy Letters, 10(2), 741-749.
Related Links
Similar Technologies
-
Lithium Iron Phosphate Battery State-of-Charge Estimation via Sine-Wave Pulses S23-521Lithium Iron Phosphate Battery State-of-Charge Estimation via Sine-Wave Pulses
-
Lithium Iron Phosphate Battery State-of-Charge Estimation via dQ/dV Analysis S23-522Lithium Iron Phosphate Battery State-of-Charge Estimation via dQ/dV Analysis
-
Digital Twin Platform for 24/7 Carbon-Free Electrified Fleet Operations S23-398Digital Twin Platform for 24/7 Carbon-Free Electrified Fleet Operations