Docket #: S24-079
Explainable Computational Methods for Predicting Treatment Response to Immunotherapy from Histology Images of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer
Non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) accounts for approximately 85% of all lung cancer cases, making it the leading cause of cancer-related deaths globally. Post-surgical recurrence and treatment resistance are the main causes of cancer-related mortality. In the past decade, immune checkpoint inhibitors have revolutionized the therapeutic landscape for NSCLC. In patients lacking targetable oncogenic driver mutations, anti-PD-1/PD-L1 antibodies have become the backbone of first-line therapy. Although several anti-PD-1/PD-L1 antibodies have demonstrated clinical benefit in NSCLC treatment, the objective response rate ranges from 27% to 45%, indicating that the treatment benefit is limited to only a subset of patients. Developing reliable approaches for predicting treatment response is essential for guiding the selection of therapeutic strategies.
Inventors at Stanford have developed a computational method, called NucSegAI, that predicts the likelihood of a patient responding to immune checkpoint inhibitor-based immunotherapy using H&E- stained histology images of tumor tissues. The method takes histology images as input and follows a four- step workflow.
- Cell Nuclei Segmentation and Classification: The method first segments cell nuclei from histology images and classifies them into five different types using a deep-learning model we developed.
- Spatial Relationship Modeling: It then models the spatial relationships between different cell types using a graph-based computational algorithm.
- Lymphocyte Classification: Lymphocytes are classified into ten distinct categories based on their morphological, textural and topological features.
- Treatment Response Likelihood Calculation: Finally, the method calculates the likelihood of treatment response based on the proportions of lymphocytes in each category.
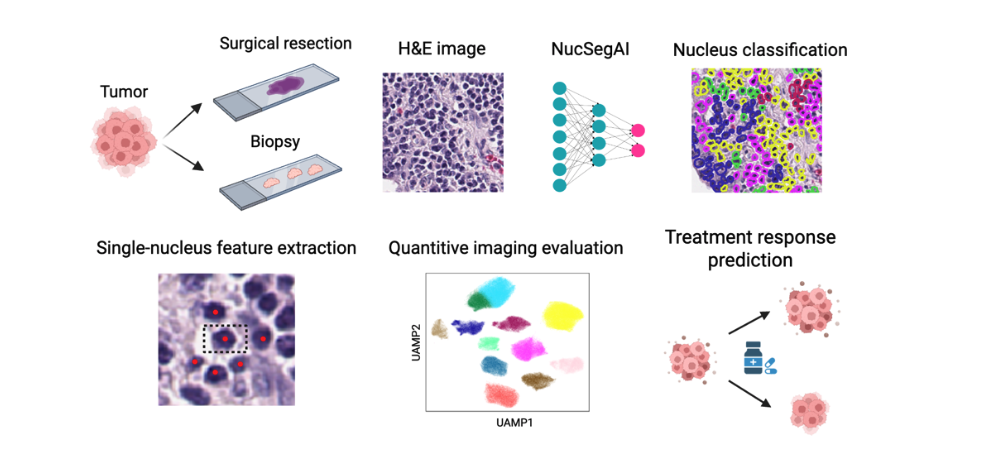
The described method has the potential to be commercialized as a tool for decision support, a service for personalized medicine, and a research tool, which will benefit biotechnology companies, pharmaceutical companies and academic researchers.
Stage of Development
Prototype
Advantages
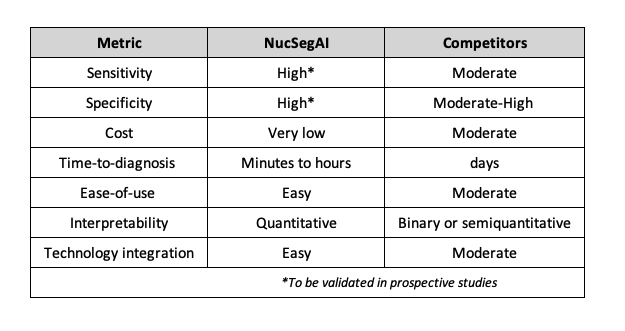
The primary competitors of NucSegAI are PD-L1 immunohistochemistry (IHC) assays, which are currently the standard companion diagnostics used to guide immunotherapy decisions in non-small cell lung cancer. Compared to these assays, NucSegAI offers several key advantages in terms of tissue requirements, predictive accuracy, cost-effectiveness and scalability, turnaround time, and interpretability (see Table 1 below).
- Input Requirements: Unlike conventional PD-L1 assays that consume valuable tissue sections and require additional staining with proprietary antibodies, NucSegAI requires routine H&E–stained slides, which are already standard in diagnostic workflows.
- Predictive Accuracy: NucSegAI demonstrates higher predictive performance compared to PD-L1 IHC assays.
- Cost and Scalability: Traditional IHC assays require specialized platforms and licensed reagents,which increase cost and limit scalability. In contrast, NucSegAI can be deployed on standard digital pathology infrastructure using only H&E images, enabling large-scale, cost-efficient analysis.
- Interpretability: Whereas PD-L1 assays provide binary or semiquantitative scores, NucSegAI outputs quantitative, spatially resolved maps of cell types and interactions.
- Automation: PD-L1 assessment typically requires manual interpretation by pathologists and is subject to inter-observer variability. NucSegAI, once trained, provides a fully automated and reproducible pipeline.
Table 1. Comparison of NucSegAI with existing products
Applications
- Clinical trial optimization
- Personalized medicine tool
- Digital pathology tool
- Immunotherapy research tool
Publications
- Zheng, Y., Sadée, C., Ozawa, M., Howitt, B. E., & Gevaert, O. (2025). "Single-cell multimodal analysis reveals tumor microenvironment predictive of treatment response in non–small cell lung cancer." Science Advances, 11(21), eadu2151.
Patent Status
Provisional Pending
Related Links
Similar Technologies
-
Microfluidic guillotine for splitting cellular structures S18-227Microfluidic guillotine for splitting cellular structures
-
'?Dicer' for Uniformly Sectioning Tissue Samples S20-435'?Dicer' for Uniformly Sectioning Tissue Samples
-
MagSweeper: high purity capture of circulating tumor cells and other rare cells S07-132MagSweeper: high purity capture of circulating tumor cells and other rare cells