Docket #: S19-130
KleinPAT: Rapid modal sound synthesis model
Stanford researchers have developed a method called KleinPAT, for creating sound models in seconds, making it cost effective to simulate sounds for many different objects in a virtual environment. KleinPAT's algorithm is low-cost, high-quality; and can synthesize realistic, synchronized sounds on-demand in real-time environments.
Initial results demonstrate that this method is 1000x to 4000x faster for objects with a few hundred vibration modes compared to previous methods, shortening the processing time from a few days to now just seconds. This invention may potentially revolutionize acoustic vibration analysis for engineering acoustics and sound synthesis in virtual environments.
Please see the KleinPAT Project website for videos and additional information.
Stanford Engineering Research & Ideas "A new algorithm enables more realistic sound effects in VR"
Figures:
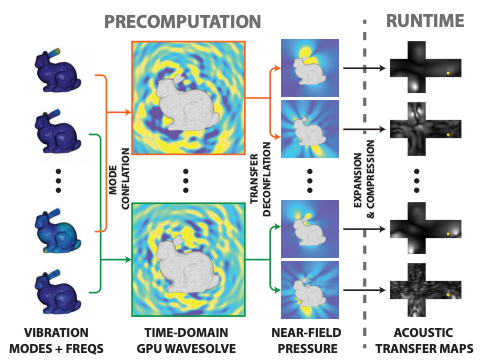
Figure description-KleinPAT Overview: Our method can evaluate acoustic transfer for 292 modes of this plastic bunny using only 6 time-domain wave simulations constructed by optimally conflating modes into 6 chords. The resulting sounds fields are deconflated to estimate the 292 transfer fields, then approximated with far-field acoustic transfer (FFAT) cube maps for real-time evaluation. This precomputed acoustic transfer (PAT) preprocess is over 4000x faster than traditional BEM-based approaches for the bunny.
Stage of Development
Prototype - The code has been tested and verified on several different 3D objects
Applications
- Virtual reality/ Augmented Reality (VR/AR) - Real-time sound synthesis for rigid-body objects in virtual environments
- Radiation analysis of vibrating structures in engineering and product design
Advantages
- Fast and real-time - new sounds can be synthesized in real-time Lower preprocessing costs - can precompute acoustic radiation fields 1000x-4000x faster than prior computer simulation methods
- Enables interactive environments with realistic sound effects
- Easily accessible content - can be used to create libraries of 500 new sounds quickly
Publications
- Jui-Hsien Wang, and Doug L. James. 2019. KleinPAT: Optimal Mode Conflation For Time-Domain Precomputation Of Acoustic Transfer. ACM Trans. Graph. 38, 4, Article 122 (July 2019), 12 pages.
Related Links
Patents
- Published Application: WO2020243517
- Published Application: 20220319483
- Issued: 12,354,579 (USA)
Similar Technologies
-
Real-time Auralization System for Virtual Spaces and On-line Meetings S18-504Real-time Auralization System for Virtual Spaces and On-line Meetings
-
Grabity: A Virtual Reality Controller that Simulates Weight and Stiffness S17-113Grabity: A Virtual Reality Controller that Simulates Weight and Stiffness
-
Pipelined chip architecture for low-cost, energy efficient machine learning on edge devices S23-084Pipelined chip architecture for low-cost, energy efficient machine learning on edge devices