Docket #: S22-088
LISA: Learning Interpretable Skills Abstractions from Language
Stanford researchers have developed a novel method (LISA) for enabling artificial agents / robots to follow natural language instructions in complex environments. There is a huge interest in robotics research to effectively decompose complex language (plain English) into simpler skills. Following natural language instructions effectively is challenging, and current methods depend on directly passing natural language instructions to an agent. Stanford researchers have developed LISA, which passes a sequence of learned ciphers (skills) to the agent instead of natural language instructions. LISA (Learning Interpretable Skills Abstractions) is a hierarchical learning framework that can learn diverse, interpretable skill abstractions from language-conditioned demonstrations of behavior by end-to-end training of deep learning models. LISA enables users to use plain English to perform complex long-horizon tasks. This novel method outperforms prior methods to complete long-range instructions with double the effectiveness. Moreover, this learned language protocol makes the behavior of a robot very interpretable, which makes it highly desirable in settings like robotic surgery, autonomous vehicles, construction robots, and other safety-critical areas. Overall, LISA can enable artificial agents or robots to perform highly complex tasks in real-world environments like homes, offices, and hospitals.
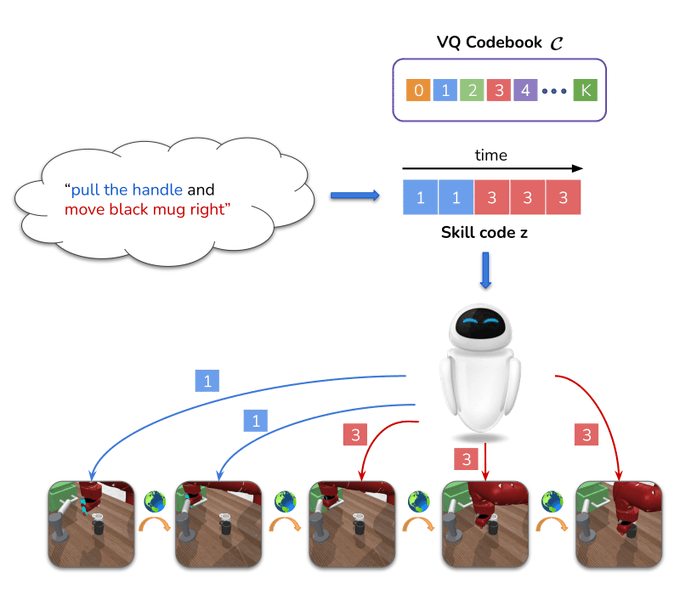
Figure 1 Description:Introducing LISA: Learning Interpretable Skill Abstractions, which learns a middle human-interpretable language protocol to condition agents.
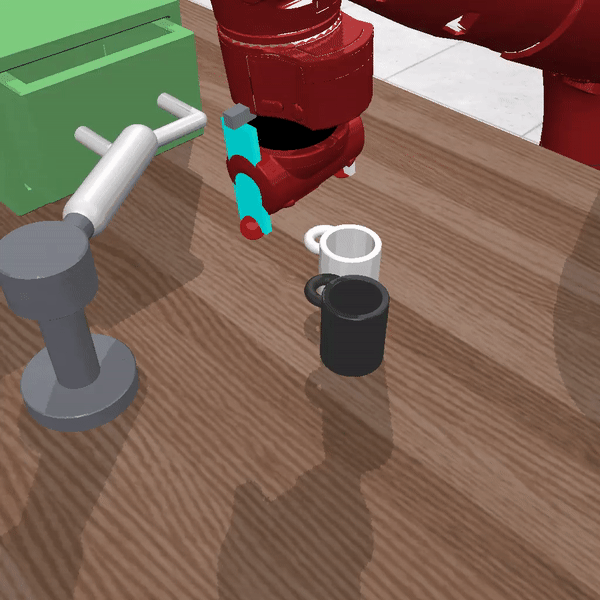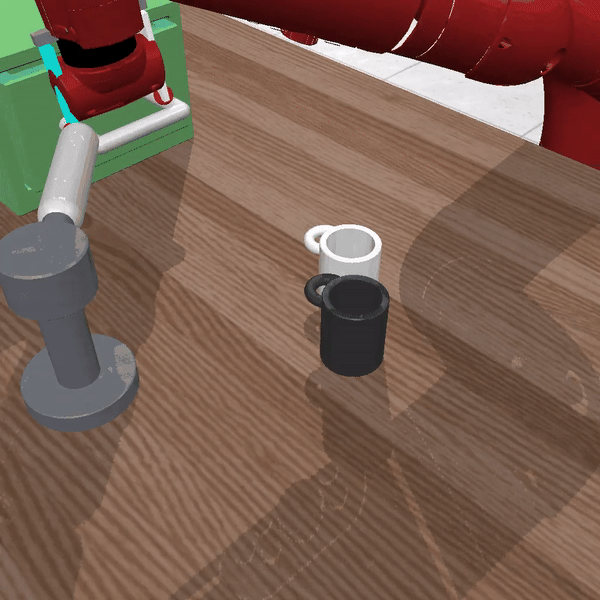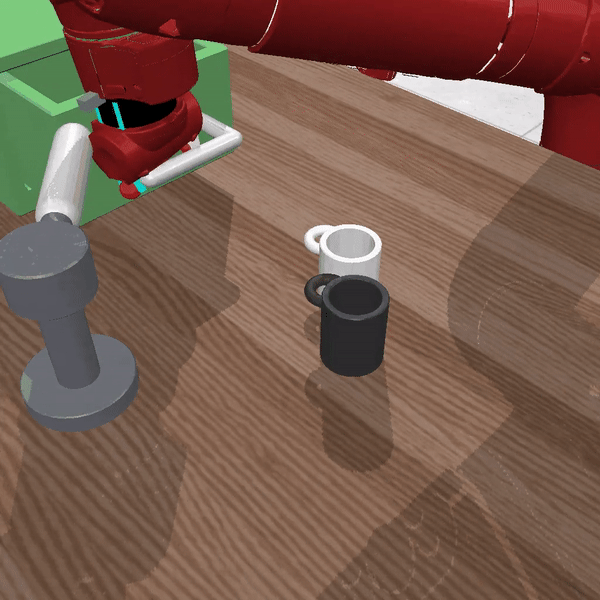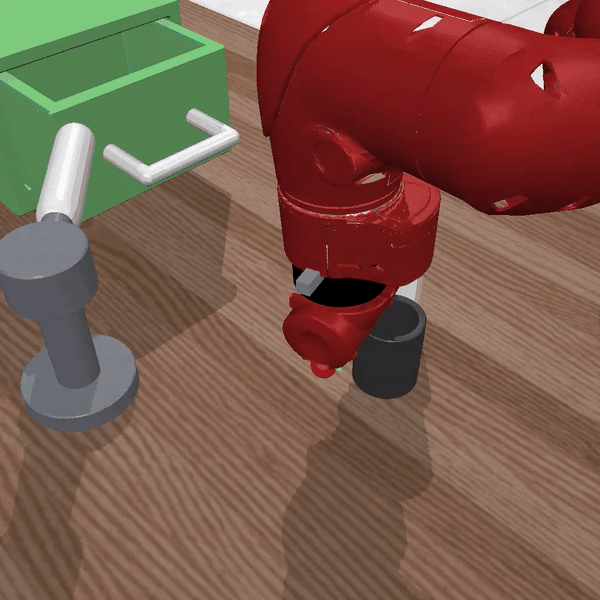
Figure 2 Description:LISA solving the command "pull the handle and move black mug right"
Stage of Development
Proof of concept
Applications
- Performance of tasks by robot in complex, real-world environments
- household helper robots
- factory robots
- construction robots
- robotic equipment in hospital/surgery settings
- autonomous vehicles
Advantages
- Improved behavior of artificial agents (>2x effective)
- Requires fewer amounts of data
- Shows good generalization to different language instructions
Publications
- Garg, D., Vaidyanath, S., Kim, K., Song, J., & Ermon, S. (2022). LISA: Learning Interpretable Skill Abstractions from Language. arXiv preprint arXiv:2203.00054.
Patents
- Published Application: 20230267284
- Issued: 12,468,902 (USA)
Similar Technologies
-
Browser Integration for Rendering Text Edits S18-282Browser Integration for Rendering Text Edits
-
Riff, a reflection assistant powered by generative AI (riffbot.ai) S24-131Riff, a reflection assistant powered by generative AI (riffbot.ai)
-
Phrasal: A Statistical Phrase-based Machine Translation System S15-036Phrasal: A Statistical Phrase-based Machine Translation System