Docket #: S19-339
Machine Learning Algorithms to Differentiate Among Pulmonary Complications After Hematopoietic Cell Transplant
Stanford researchers have developed machine learning algorithms to characterize and diagnose lung graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) subtypes from volumetric chest computed tomography (CT). Pulmonary complications, including infections chronic graft-vs-host disease, are highly prevalent in patients after hematopoietic cell transplantation, but distinguishing between these conditions clinically is challenging and can lead to delayed diagnosis and treatment. A quantitative method to differentiate among these pulmonary diseases can augment providers' abilities to act more quickly and with greater precision in delivering targeted therapy.
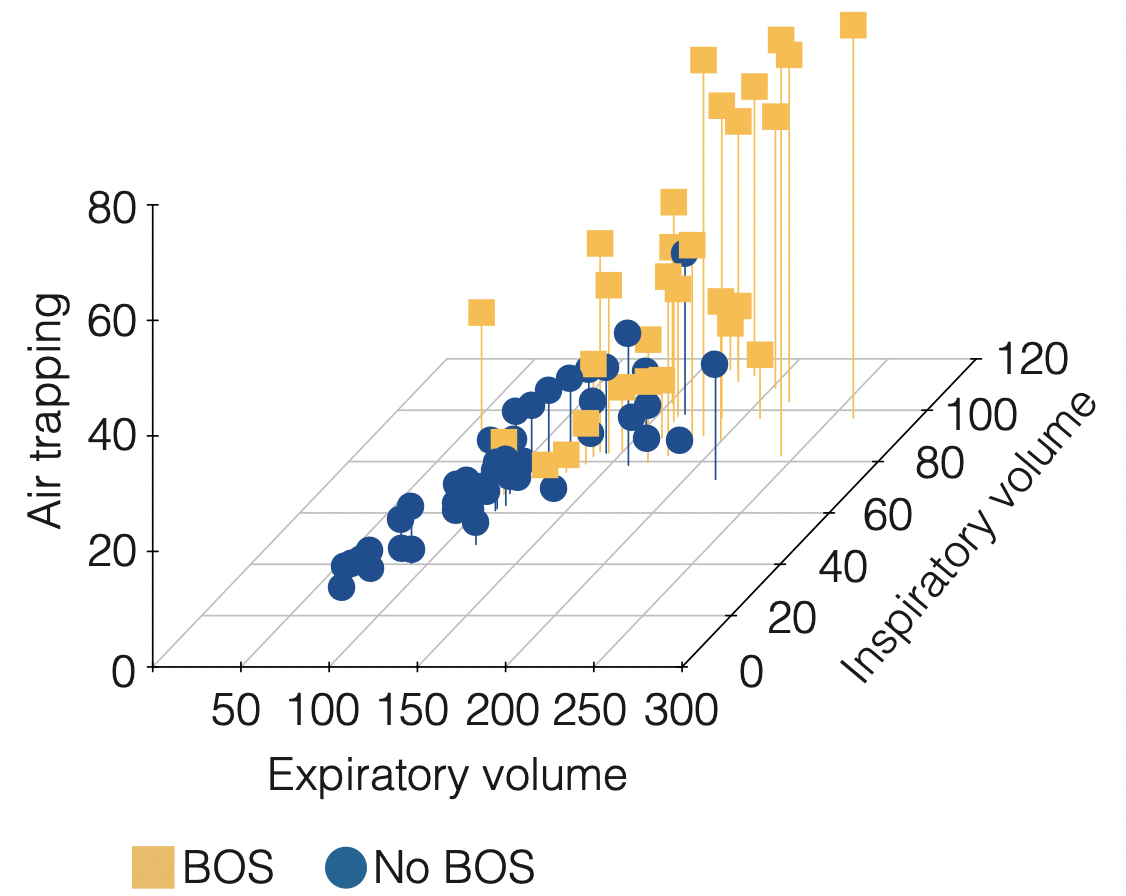
The graphic above and the interactive, three dimensional figure below illustrate the separation of patients with BOS versus patients who do not have BOS, exclusively by the percentage of air trapping in their lungs and their inspiratory and expiratory lung volumes when adjusted for percentage predicted. Additional clinical data are not used and not required to allow for classification of patients into distinct categories that assist in critical management decisions by clinicians.
The interactive, three dimensional figure at the site listed below shows the distinct spread of four clusters of patients who have received stem cell transplant and who split into categories that represent clinically distinct phenotypes of sclerotic skin from GVHD (cluster 1), normal lung (cluster 2), early BOS (cluster 3), moderate and advanced BOS (cluster 4).
Three dimensional results of clustering analysis of volumetric CT chest
Stage of Development
Applications
- Diagnosis of early lung GVHD and other subtypes of pulmonary complications after HCT.
Advantages
- Novel- There are currently limited quantitative or algorithmic approaches to address this clinical challenge in a reproducible, scalable manner.
- Can distinguish subtypes which require different therapies, which are emerging and are being actively researched in academic and commercial settings.
- Earlier diagnosis enabling more precise treatment and better outcomes in a high risk patient population with a high risk of morbidity and death from these conditions.
- Earlier and more precise diagnosis allows for less costly intervention and reduction of complications that produce tremendous financial strain on medical centers.
Publications
- Sharifi, Husham, Yu Kuang Lai, Henry Guo, Mita Hoppenfeld, Zachary D. Guenther, Laura Johnston, Theresa Brondstetter, Laveena Chhatwani, Mark R. Nicolls, and Joe L. Hsu. "Machine learning algorithms to differentiate among pulmonary complications after hematopoietic cell transplant." Chest 158, no. 3 (2020): 1090-1103.
- Sharifi, H.*, Guenther, Z.*, Leung, A.N.C., Johnston, L., Lai, Y.K., Hsu, J.L., Guo, H.H. "Head-to-head Comparison of Qualitative Radiologist Assessment With Automated Quantitative Computed Tomography Analysis for Bronchiolitis Obliterans Syndrome After Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation." Journal of Thoracic Imaging Accepted and in press, 2021 May 12.
Related Links
Patents
- Published Application: 20220039770
Similar Technologies
-
Radiotransparent audio-visual system to avoid pediatric patient anesthesia during radiation therapy and imaging. S23-306Radiotransparent audio-visual system to avoid pediatric patient anesthesia during radiation therapy and imaging.
-
Deep Learning Enabled Hybrid CT-MRI with Highly Sparse Sensory Data S21-073Deep Learning Enabled Hybrid CT-MRI with Highly Sparse Sensory Data
-
Automated coronary artery calcification (CAC) scoring S20-124Automated coronary artery calcification (CAC) scoring