Docket #: S20-310
Method for Calculating the Marginal Energy Intensity of Water Supply for Users
This methodology computes the marginal energy utilization for supplying individual water users based on the existing topology of the water distribution network (WDN), pipe sizes and baseline flows. By breaking down the marginal energy intensity (MEI) into components from transmission, treatment and distribution of water, stage specific cost and energy utilization can be calculated. Specifically, MEI values are calculated by backtracking a given customer's inflow to its sources, including tanks that temporarily hold and mix water. This can be modeled as a function of the time of day, accounting for embedded energy of the water system and allows utility companies to minimize operating costs while maintaining water quality. A water quality estimation tool can be combined with the above algorithm to yield a multi-objective optimization for water quality and public health.
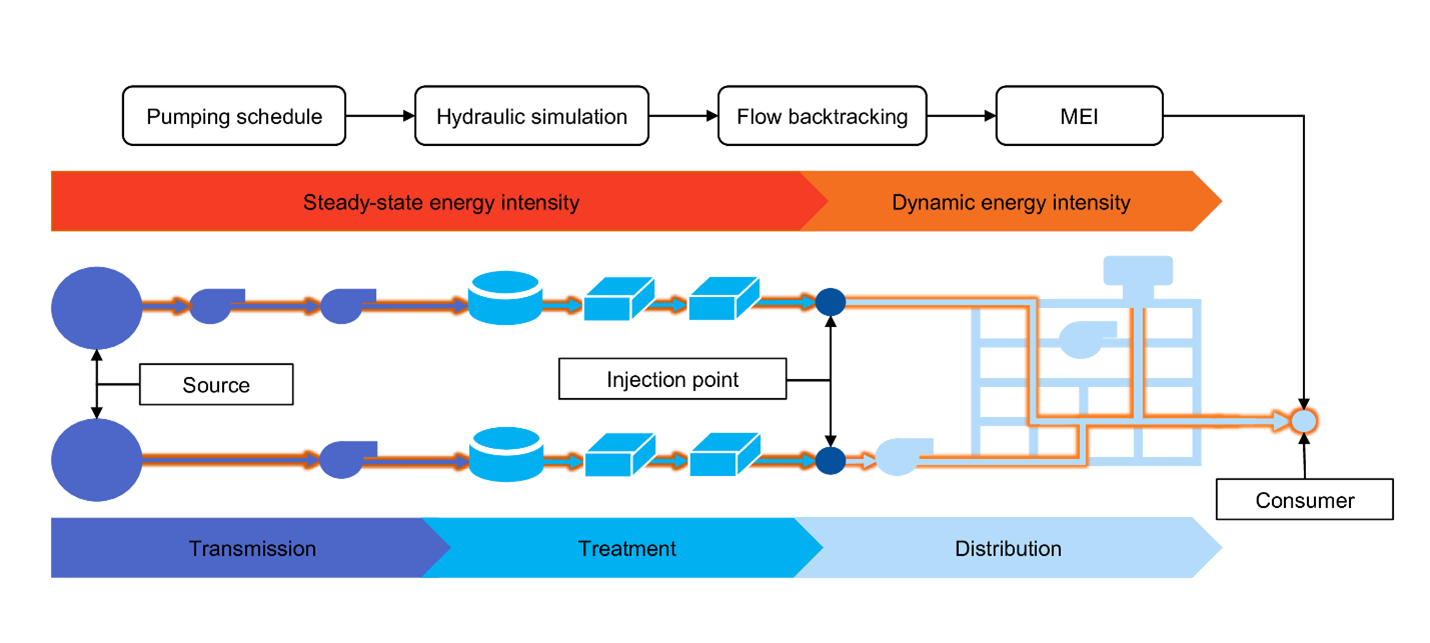
Photo description: composition of MEI and the schematic of its computation.
Stage of Research
Applications
- Set efficient spatial, temporal, and elevation specific variable water prices
- Prioritize and inform the value of water efficiency upgrades
- Determine magnitude and value of electric grid demand response by end water users
- Optimize water quality in combination with marginal energy intensity minimization
Advantages
- Handles multi-source/injection point WDNs to separately establish fair water distribution markets
- Post-pump scheduling computation
- Real time water quality and carbon intensity
- Computes water reuse, water efficiency, demand response, and water use timing shift potentials
Related Links
Patents
- Published Application: WO2022039963
- Published Application: 20240010537
Similar Technologies
-
Predictive Control Platform for Wastewater Treatment Energy Storage and Generation S21-048Predictive Control Platform for Wastewater Treatment Energy Storage and Generation
-
Data-Driven Urban Energy Benchmarking of Buildings (DUE-B) S17-505Data-Driven Urban Energy Benchmarking of Buildings (DUE-B)
-
Concrete Durability Modeling Software for Building Information Models S19-149Concrete Durability Modeling Software for Building Information Models