Docket #: S17-231
Nanoparticle platform to activate self-specific CD8+ T cells to improve antitumor immune response
Researchers at Stanford have developed a nanoparticle-based platform to enhance activation of self-specific CD8+ T cells in the tumor microenvironment to fight cancer while minimizing toxic side effects. Cancer immunotherapies have been developed to modulate the body's immune system to fight its own cancer. However, there can be challenges with these therapies including systemic toxicity and an inability to activate self-specific CD8+ T cells. To overcome these challenges and enable sustained immune activation in the tumor microenvironment the inventors have developed this technology. It provides PLGA nanoparticles functionalized with anti-CD28 antibody to deliver immunostimulants, including IL-2, TLR2 agonist and NOD2 agonist, in a controlled manner. This nanoparticle platform enables the immunostimulants to be released at the tumor site to activate self-specific CD8+ T cells to fight the cancer. Furthermore, this localized delivery minimizes potential systemic toxicities. This technology provides the means to enhance the antitumor immune response.
Figure:
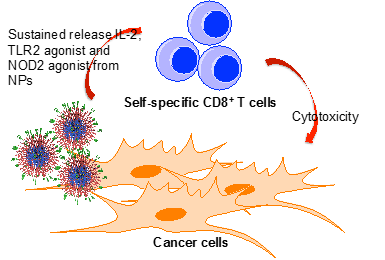
Applications
- Cancer immunotherapy
Advantages
- New strategy for in situ activation of self-specific CD8+T cells to fight cancer
- Nanoparticle platform:
- Protects cargos from proteases
- Allows for targeted sustained release of immunostimulants
- Minimizes systemic toxicities
- Allow easy surface modification- including labeling for in vitro and in vivo tracking
- PLGA is an FDA approved biodegradable polymer with excellent biocompatibility
- Fabrication of PGLA nanoparticle is low cost and easily achievable
Publications
- Yin Q, Yu W, Grzeskowiak CL, Li J, Huang H, Guo J, Chen L, Wang F, Zhao F, von Boehmer L, Metzner TJ, Leppert JT, Chien YH, Kuo CJ, Davis MM. Nanoparticle-enabled innate immune stimulation activates endogenous tumor-infiltrating T cells with broad antigen specificities. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 May 25;118(21):e2016168118.
Related Links
Patents
- Published Application: WO2019023622
- Published Application: 20200164090
- Issued: 11,925,693 (USA)
Similar Technologies
-
Engineered proteins to enhance the sensitivity of immune cells to IL-2 S17-190Engineered proteins to enhance the sensitivity of immune cells to IL-2
-
Agents to induce immunogenicity and improve efficacy of anti-cancer therapeutics S15-434Agents to induce immunogenicity and improve efficacy of anti-cancer therapeutics
-
Enhanced activation of CD8+ and CD4+ T cells by a vaccine targeting CD244 or CD48 S20-039Enhanced activation of CD8+ and CD4+ T cells by a vaccine targeting CD244 or CD48