Docket #: S24-421
Neuromonitoring-guided cognitive intervention for targeted enhancement of working memory networks
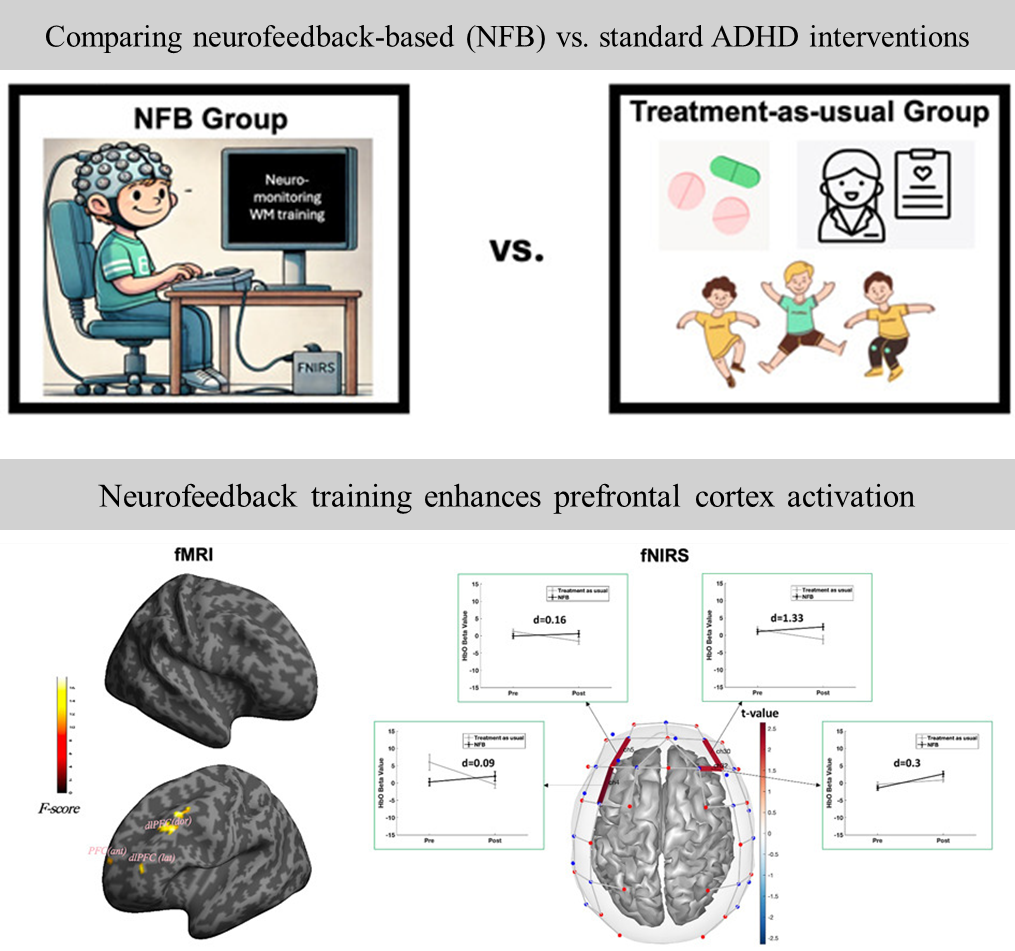
Stanford researchers have developed a neuromonitoring-guided cognitive intervention that enhances working memory by dynamically identifying and reinforcing engagement of individualized brain networks in real time.
Traditional cognitive training tools often lack specificity and adaptability, offering limited benefit for neurodiverse populations such as individuals with ADHD. These approaches typically fail to monitor neural engagement or account for differences in brain function across individuals.
This innovative platform integrates real-time functional neuroimaging, adaptive neurofeedback, and personalized cognitive exercises into a closed-loop system. As users complete working memory tasks, the system continuously monitors brain activity and reinforces strategies that optimally activate the target network. By accounting for individual variability in neural circuitry, the intervention ensures precise localization and engagement of the desired brain regions.
Validated in children with ADHD in a pre-registered clinical trial study, the technology has shown improvements in attention, focus, and cognitive control. Its personalized, brain-guided approach has broad potential beyond ADHD, including applications in learning disabilities, cognitive rehabilitation, and digital mental health.
By linking neural data to behavioral feedback in real time, this platform offers a personalized cognitive enhancement, enabling targeted, scalable, and clinically meaningful digital therapeutics.
The research team is currently working on a wearable neuroimaging platform to be able to deliver this intervention at home to increase scalability.
Applications
- Enhancing working memory and cognitive control in individuals with ADHD
- Personalized cognitive rehabilitation for individuals with working memory deficits due to neurological or psychiatric conditions
- Development of adaptive digital therapeutics for neurodiverse populations
Advantages
- First intervention to target working memory networks using real-time neuromonitoring and neurofeedback
- Outperforms existing computerized training by adapting to individual brain activity in real time
- Enables personalized, closed-loop modulation of brain function for higher efficacy
- Scalable as a non-invasive, software-based digital therapeutic platform
Publications
- Jounghani, A. R., Gozdas, E., Dacorro, L., Avelar-Pereira, B., Reitmaier, S., Fingerhut, H., ... & Hosseini, S. H. Neuromonitoring-guided working memory intervention in children with ADHD. 2024 iScience, 27(11).
- Rahimpour Jounghani, A., Kumar, A., Moreno Carbonell, L. et al. Wearable fNIRS platform for dense sampling and precision functional neuroimaging. npj Digit. Med. 8, 271 (2025).
- Rahimpour Jounghani, Ali. Revolutionizing ADHD Treatment Through Neuromonitoring-Guided Working Memory Interventions. Stanford Chemical Engineering News, 2025.
- Digitale, Erin Digital tool gives kids with ADHD real-time feedback on their brains. Stanford Report, 2025.
- Digitale, Erin Digital tool gives kids with ADHD real-time feedback on their brains. Stanford Medicine News, 2025.
Related Links
Similar Technologies
-
Using a probabilistic model to infer target labels for unsupervised BCI recalibration S22-226Using a probabilistic model to infer target labels for unsupervised BCI recalibration
-
Neural Decoding of Attempted Speech S22-286Neural Decoding of Attempted Speech
-
FIP microscope for simultaneous multi-site measurement of neuronal circuit dynamics S15-390FIP microscope for simultaneous multi-site measurement of neuronal circuit dynamics