Docket #: S15-080
A Photosynthetic System for Treatment of Ischemic Tissue
Stanford researchers have patented a photosynthetic system using a cyanobacterium solution that can be delivered to ischemic tissues, where blood flow is insufficient. This addresses a major clinical problem for patients with heart and vascular diseases. The solution provides glucose and oxygen while removing carbon dioxide, enabling light to sustain the tissue. This low-cost, simple solution can treat myocardial ischemia and infarction, protect the heart during cardiopulmonary bypass surgery, and preserve organs during transportation.
Figure
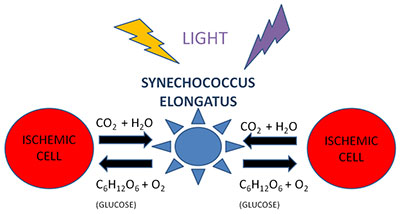
Figure description: Photosynthetic system
Stage of Research:
- Conducted large animal translational model of myocardial protection utilizing this photosynthetic strategy at Stanford
- Results showed that targeted intramyocardial delivery of a photosynthetic agent to ischemic territory enables localized oxygen production, enhanced metabolic activity, and augmented ventricular function in a rat model of acute myocardial ischemia.
On-going Research:
- Improving delivery device for enhanced clinical translatability
Applications
- Treatment of myocardial ischemia
- Myocardial protection during cardiopulmonary bypass
- Organ preservation for transplantation
- Treatment of acute and chronic peripheral vascular disease
Advantages
- Low cost relative to stent placement and/or open surgery
- Direct oxygen delivery to muscle at risk without necessarily addressing restoration of blood flow
- Can supply tissue with energy even in patients that otherwise cannot be revascularized either surgically or with stent placement
- Can extend the time that an organ could be transported prior to transplantation, thereby increasing the available patient pool and enhancing outcomes following transplantation
- Could provide a superior treatment for peripheral vascular disease. Specifically, distal revascularization (below the knee) demonstrates modest results at best, whereas this treatment offers a completely novel and potentially superior approach.
Publications
- Cohen, Jeffrey E., Andrew B. Goldstone, Michael J. Paulsen, Yasuhiro Shudo, Amanda N. Steele, Bryan B. Edwards, Jay B. Patel et al. "An innovative biologic system for photon-powered myocardium in the ischemic heart." Science advances 3, no. 6 (2017): e1603078.
- Goldstone, Andrew B., Jeffrey E. Cohen, Yasuhiro Shudo, Amanda N. Steele, Michael S. Hopkins, Jay B. Patel, Bryan B. Edwards et al. "A Light-powered Symbiosis With a Primordial Chloroplast Attenuates Myocardial Injury in the Absence of Blood Perfusion." Circulation 132, no. Suppl 3 (2015): A16907-A16907.
Related Links
Patents
- Published Application: 20160310547
- Issued: 10,137,158 (USA)
Similar Technologies
-
Transcription Factor-Driven hiPSC Differentiation Platform for 3D Cardiac Tissue Engineering S25-026Transcription Factor-Driven hiPSC Differentiation Platform for 3D Cardiac Tissue Engineering
-
Prediction of RNA structure with equivariant neural networks S21-193Prediction of RNA structure with equivariant neural networks
-
A method to generate cardiac pericytes from human induced pluripotent stem cells S22-436A method to generate cardiac pericytes from human induced pluripotent stem cells