Docket #: S12-397
Planar, Single-walled Carbon Nanotube Photodetector
Stanford researchers have patented a planar, single-walled carbon nanotube (SWNT) photodetector that maintains high carrier mobility, unlike conventional carbon nanotube network approaches. Device sensitivity is enhanced by electron acceptor or donors attached to the surface of the SWNTs. Infrared light generates electron-hole pairs in the SWNTs (140). The light adsorbent electron acceptor or donor layer (160) then accepts electrons from, or donates electrons to the SWNTs, dopes the SWNTs to p or n-type, and increases the sensitivity of SWNTs to light. The aligned SWNTs maintain high carrier mobility. The end result is a light-weight, flexible, robust, transparent, and low-cost infrared light sensor with high sensitivity.
Stage of Research
Stanford researchers demonstrated a SWNT/C60-based phototransistor. Future work will include optimizing the heterojunction, and maximizing IR absorption and carrier mobility through densely aligned SWNTs.
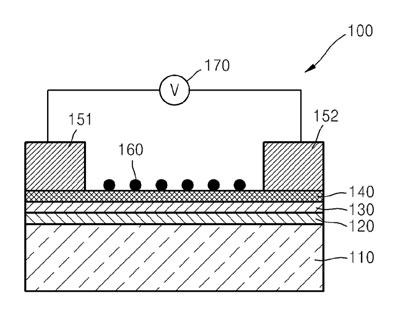
Schematic of Planar, Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube Photodector where:
110 is substrate (metal, semiconductor, glass or plastic)
120 insulation layer/gate insulation layer (Silicon oxide or silicon nitride)
130 self-assembled monolayer (SAM)
140 semiconducting single walled carbon nanotubes
151 first electrode
152 second electrode
160 light adsorbent (quantum dot, an organic dye, or an inorganic sensitizer) that is also may be an electron acceptor (fullerene or a fullerene derivative ) or an electron donor
Applications
- Solar cells and Photodetectors with end user applications in:
- Motion detectors
- Night vision devices
- Telecommunications
- Imaging sensors / remote sensing
Advantages
- Increased sensitivity compared to previous SWNT-based devices
- Low cost
- Light-weight, flexible and robust
- Transparent
- CMOS fabrication compatible
- Simple architecture
Publications
- S. Park, S. J. Kim, J. H. Nam, G. Pitner, T. H. Lee, A. L. Ayzner, H. Wang, S. W. Fong, M. Vosgueritchian, Y. J. Park, M. L. Brongersma, Z. Bao, "Significant Enhancement of Infrared Photodetector Sensitivity using Semiconducting Single-walled Carbon Nanotube/C60 Phototransistor", Adv. Mater., 27, 759-765, 2014.
Related Links
Patents
- Published Application: 20140319461
- Issued: 9,147,845 (USA)
Similar Technologies
-
STRETCHABLE SELF-HEALING POLYMERIC DIELECTRICS CROSSLINKED THROUGH METAL-LIGAND COORDINATION S17-167STRETCHABLE SELF-HEALING POLYMERIC DIELECTRICS CROSSLINKED THROUGH METAL-LIGAND COORDINATION
-
Stretchable Semiconductor via Polymer Blending S15-438Stretchable Semiconductor via Polymer Blending
-
Skin-like, Wearable Pressure Sensor S14-024Skin-like, Wearable Pressure Sensor