Docket #: S18-485
Pluripotent-specific, inducible safety switch to eliminate residual stem cells following differentiation
Despite their rapidly expanding therapeutic potential, human pluripotent stem cell (hPSC)-derived cell therapies continue to have serious safety risks. Transplantation of hPSC-derived cell populations into preclinical models has generated teratomas (tumors arising from undifferentiated hPSCs), unwanted tissues, and other types of adverse events. Thus, it is essential to ensure that all cells have been sufficiently differentiated prior to engraftment. However, it is impossible to ensure that protocols have successfully differentiated 100% of cells. Toward this end, the Porteus Lab engineered a general platform to improve the safety of future hPSC-derived cell transplantation therapies. Using genome editing via a combined CRISPR/AAV6 method, they developed hPSC lines with two drug-inducible safeguards. Clinically relevant small molecules can then selectively activate the respective safeguards to initiate cell-specific apoptosis, removing unwanted differentiated cells (via the NANOG-linked switch) or all cells in the case of an adverse event (via the ACTB-linked switch). These safe-guards provide orthogonal safety switches to address major safety concerns with pluripotent cell-derived therapies.
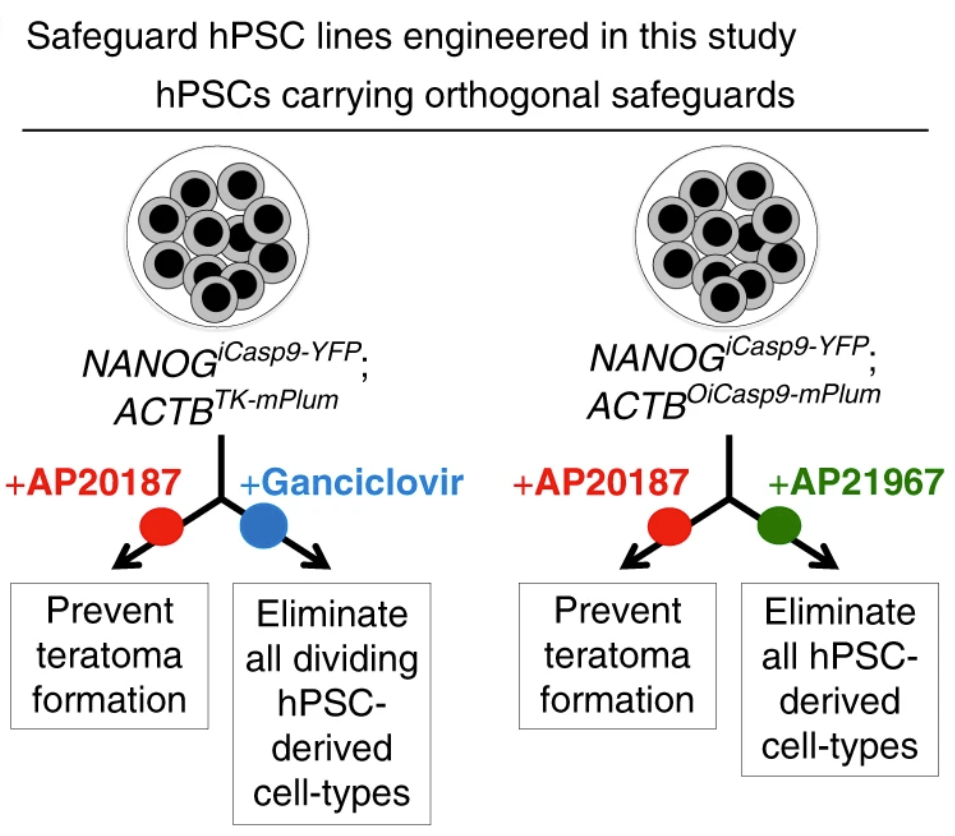
Figure caption: Safeguards engineered within hPSC lines to prevent teratoma formation and eliminate unwanted cell-types
Applications
- -Stem cell and tissue models
- -Cell therapy
- -Tissue engineering
Advantages
- -Eliminates residual pluripotent cells following differentiation
- -Controlled regulation of stem cell cultures
- -Simple integration via gene editing technologies
Publications
- Martin, R. M., Fowler, J. L., Cromer, M. K., Lesch, B. J., Ponce, E., Uchida, N., Nishimura, T., Porteus, M. H., & Loh, K. M. (2020). " Improving the safety of human pluripotent stem cell therapies using genome-edited orthogonal safeguards." Nature communications, 11(1), 1-14.
Related Links
Patents
- Published Application: WO2021173449
- Published Application: 20230085945
Similar Technologies
-
Using Minicircle DNAs to Generate Viral-Free Induced Pluripotent Cells S09-309Using Minicircle DNAs to Generate Viral-Free Induced Pluripotent Cells
-
Rapid iPS Cells from Adult Human Adipose Stem Cells S08-438Rapid iPS Cells from Adult Human Adipose Stem Cells
-
Transcription Factor-Driven hiPSC Differentiation Platform for 3D Cardiac Tissue Engineering S25-026Transcription Factor-Driven hiPSC Differentiation Platform for 3D Cardiac Tissue Engineering