Docket #: S25-117
Pre-Plied Double-Double (PPDD) Laminated Composite Tape with Short Fiber
The Stanford team has developed a Short Fiber Pre-Plied Double-Double (PPDD) Tape that can achieve complex, double-curvature composite parts like a helmet while maintaining high stiffness and other desired mechanical properties. This innovation is ideal for molded composite components in sporting goods, automotive, electronics, and medical devices, providing superior stiffness at a fraction of the weight than metals.
Components with complex curvatures require short fiber composites, as traditional long fibers resist abrupt directional changes. Conventional methods use chopped fibers that are either randomly oriented or painstakingly aligned, leading to an inefficient process that is difficult to tailor for diverse application needs.
The inventors have devised a process that begins with unidirectional prepreg tape and strategically slits the fibers in patterns that enhance formability while retaining structural integrity. This method requires just two automated steps: 1) slitting the unidirectional material and 2) stacking it into pre-plied double-double tape or sheet.
This approach maintains high fiber volume with natural uniformity while preserving approximately 80% of original strength, allowing customizable patterns for specific component requirements beyond traditional quasi-isotropic configurations. This technology creates opportunities to optimize components with complex geometries, reducing weight, production time, and costs. The application potential spans numerous industries, starting with optimum long fiber designs and transitioning to short fiber versions only when forming constraints demand it.
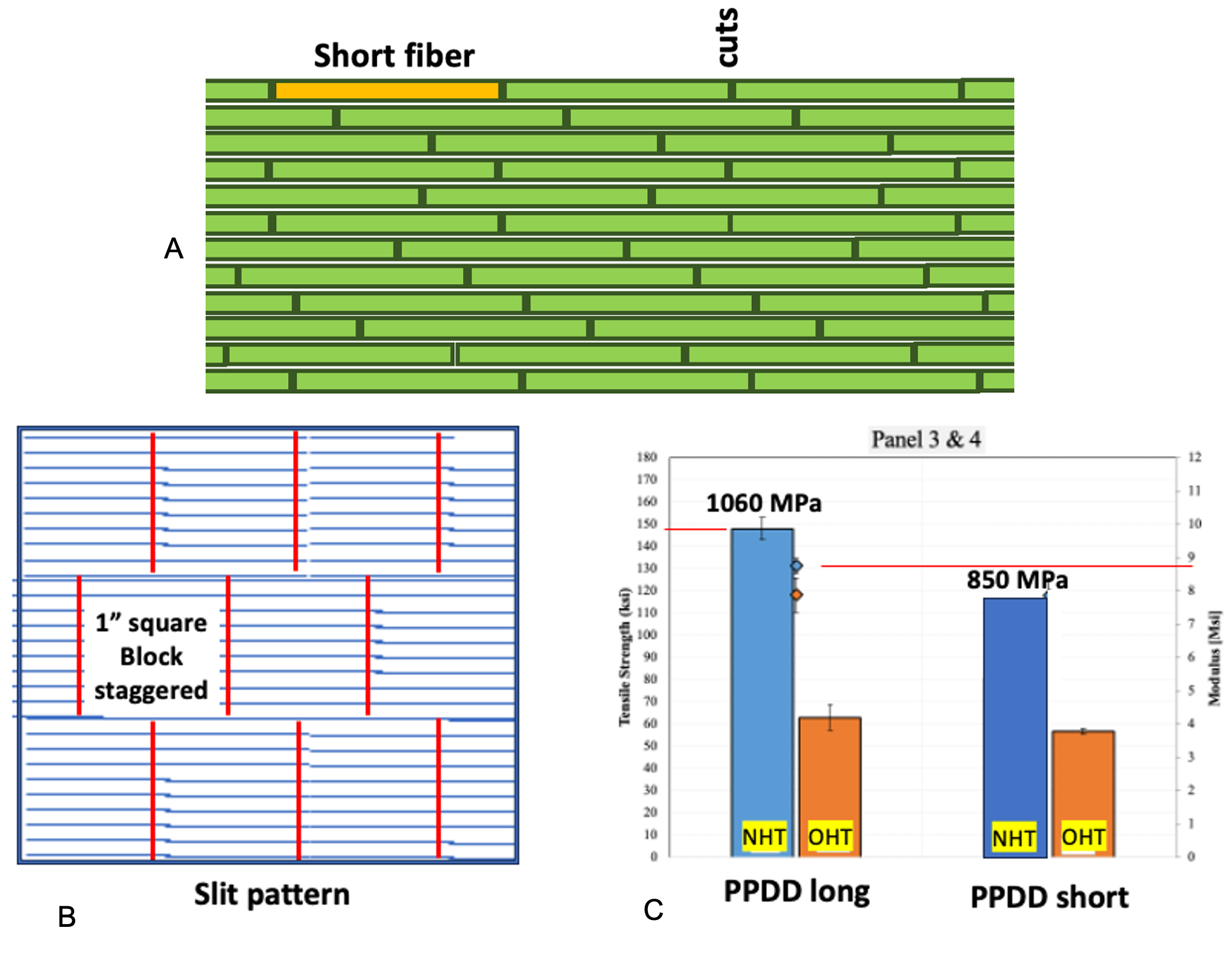
A) Prepreg tape alignment with conventional methods, B) Optimized slit pattern alignment with PPDD composite tape method, C) High tensile strength of PPDD tape in the long and short configurations
Image credit: inventors
Stage of Development: Proof of Concept
Applications
- Composite components made with molding
- Sporting protective devices
- Automotive components
- Electronic and medical devices
- Consumer products
Advantages
- High stiffness, low weight: Maintains high fiber volume, leading to less resin and less weight while maintaining high stiffness
- High strength: Preserves approximately 80% of original strength even in complex curved parts of a design due to optimized slit pattern
- Custom formability: Allows for customizable slit patterns based on component requirements
- Enables more design flexibility beyond quasi-isotropic configurations
- Support and training on the method available from the scientific team to help apply the method in a particular application
Publications
- Tsai, Stephen W. "Double–Double: New Family of Composite Laminates." AIAA Journal 59.11 (2021): 4293-4305.
Related Links
Similar Technologies
-
Manufacturing of Composite Grid/Core/Skin Structures S19-225Manufacturing of Composite Grid/Core/Skin Structures
-
Stanford Drone Dataset: Multi-scale, Multi-target social navigation S17-376Stanford Drone Dataset: Multi-scale, Multi-target social navigation
-
Negative Thermal Expansion for Glueless Sleave Joints S22-031Negative Thermal Expansion for Glueless Sleave Joints