Docket #: S23-508
Pressure as a Second Driving Force to Overcome Diffusion Limitations in Encapsulated Islet Cell Therapy
Researchers at Stanford have found that applying pressure to macroencapsulation can enhance insulin transport from encapsulated islet beta cells to surrounding tissue and assist in glucose metabolism in type 1 diabetes (T1D) patients.
T1D is an autoimmune disease in which insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas are destroyed by the patient's own immune system. The resulting insulin deficiency is most often managed through exogenous insulin administration. This requires frequent or constant blood glucose level monitoring and insulin administration, significantly diminishing the patient's quality of life. Many studies have suggested transplantation of macroencapsulated islet beta cells as a means to achieve insulin independence. The encapsulation can provide a robust barrier against the host immune system. However, it could also impede insulin diffusion from the encapsulation, making it difficult to release insulin at physiological levels.
Stanford researchers have discovered that applying pressure to the macroencapsulation could enhance insulin transport kinetics. A modest pressure equivalent to normal diastolic blood pressure sufficiently improved insulin flux across encapsulating membranes. Both in vitro and in vivo experiments have shown that pressure-driven flow is superior to relying solely on diffusion. Transplantation of the pressurized macroencapsulation of beta islets could help T1D patients achieve full insulin independence.
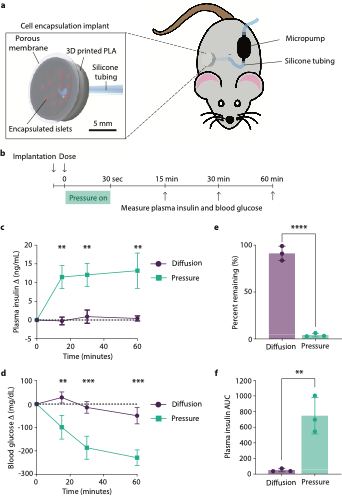
Figure Caption: Pressure-driven dosing from macroencapsulated islets supporting physiologic insulin dosing in mice
Applications
- Cadaveric, donor, or stem cell-derived beta islet transplantation
- Artificial pancreas
- In vivo cell-based bioelectronics
Advantages
- Improved transport of islet cells compared to diffusion-based macroencapsulation devices
- Complete immunoisolation
- Retrievable
- Precise temporal regulation of insulin delivery
Publications
- Thomson, E. A., Lal, R. A., et al. (2023). "Pressure-Driven Insulin Release Overcomes Limitations of Diffusion for Encapsulated Islet Cell Therapy." bioRxiv : the preprint server for biology, 2023.12.11.570688.
- Thomson, E. A., Xu, H., et al. (2024). "?-Cells as a Cell Factory for On-Demand Recombinant Protein Dosing: Harnessing the Neuroendocrine Cell Secretory Pathway for Controlled Release." bioRxiv : the preprint server for biology, 2024.01.20.576492.
Related Links
Patents
- Published Application: 20250177644
Similar Technologies
-
A Method to Regulate Protein Function in Living Cells Using Small Molecules S06-024A Method to Regulate Protein Function in Living Cells Using Small Molecules
-
Dual-Agent Conditioning Improves Hematopoietic Stem Cell Engraftment S20-361Dual-Agent Conditioning Improves Hematopoietic Stem Cell Engraftment
-
Simplified Generation and Purification of Human Primordial Germ-Like Cells S20-093Simplified Generation and Purification of Human Primordial Germ-Like Cells