Docket #: S23-543
Reducing DNA/RNA Sequence Dropout with Predictive Synthesis Models
Stanford researchers have developed a method using trained learning models to optimize synthetic DNA libraries for high-throughput molecular biology experiments. This approach ensures more uniform sequence coverage by using predictive models to avoid sequence "dropout" caused by synthesis and downstream workflows.
High-throughput experiments, such as CRISPR screens and synthetic RNA/DNA testing, often face challenges where many sequences are lost during the final sequencing readout. This occurs because sequences with higher read potential can dominate those with lower potential, reducing overall efficiency and leading to financial waste. Stanford scientists have developed predictive models, or "oracles," to predict sequence performance and split oligonucleotide pools into subpools.
The method applies to a wide range of biological research areas, including CRISPR screens, synthetic biology, gene synthesis, DNA-based storage, and reporter systems. Researchers can guide the subpool-splitting process using pilot experiments or AI-driven predictions tailored to specific workflows.
Figure
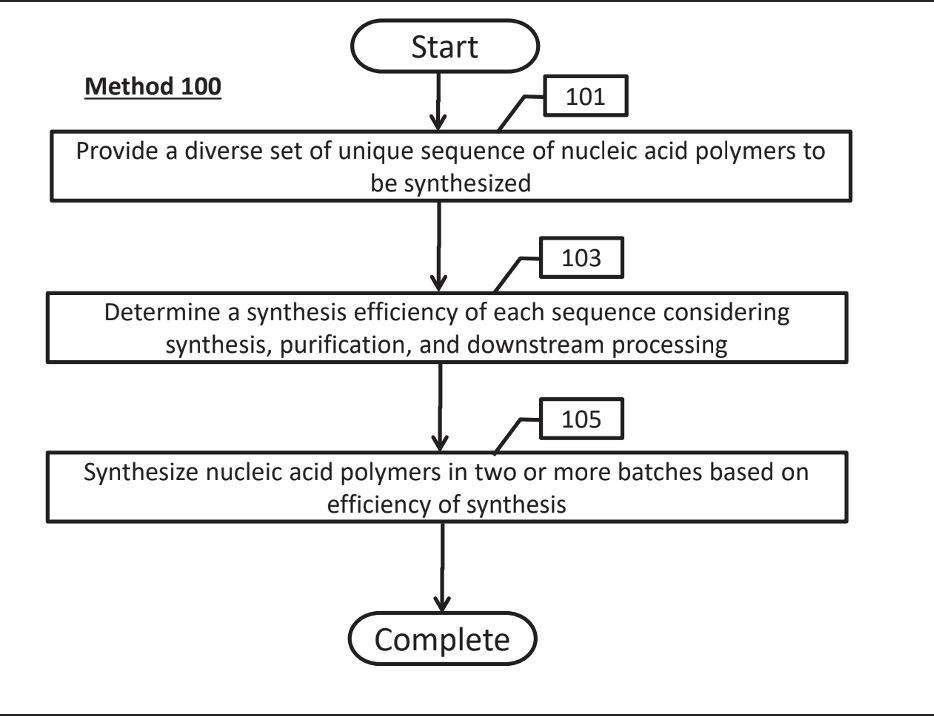
Stage of Development:
Proof of concept
Applications
- Oligonucleotide synthesis
- Single guide RNA synthesis
- Gene synthesis
Advantages
- Cost effective
- Improved synthesis outputs
- RNA/DNA applicable
Publications
- Shujun He, Rui Huang, Jill Townley, Rachael C. Kretsch, Thomas G. Karagianes, David B.T. Cox, Hamish Blair, Dmitry Penzar, Valeriy Vyaltsev, Elizaveta Aristova, Arsenii Zinkevich, Artemy Bakulin, Hoyeol Sohn, Daniel Krstevski, Takaaki Fukui, Fumiya Tatematsu, Yusuke Uchida, Donghoon Jang, Jun Seong Lee, Roger Shieh, Tom Ma, Eduard Martynov, Maxim V. Shugaev, Habib S.T. Bukhari, Kazuki Fujikawa, Kazuki Onodera, Christof Henkel, Shlomo Ron, Jonathan Romano, John J. Nicol, Grace P. Nye, Yuan Wu, Christian Choe, Walter Reade, Eterna participants, Rhiju Das. Ribonanza: deep learning of RNA structure through dual crowdsourcing. bioRxiv 2024.02.24.581671 (Preprint).
Related Links
Patents
- Published Application: WO2025137352
Similar Technologies
-
Non-Silencing Plasmid Vectors for Sustained High Level Expression of Transgenes S14-381Non-Silencing Plasmid Vectors for Sustained High Level Expression of Transgenes
-
Optoelectronic orchestrated microdroplet reactors for solid-phase reactions S24-293Optoelectronic orchestrated microdroplet reactors for solid-phase reactions
-
Optimized Synthesis of RNA-based Therapeutic Candidates S20-175Optimized Synthesis of RNA-based Therapeutic Candidates