Docket #: S18-183
StcE- a mucin specific protease
Researchers at Stanford have identified the bacterial protease, StcE, as a much-needed tool for the analysis of mucin-domain glycoproteins (mucins). Mucin domains are densely o-glycosylated modular protein domains that are found in a wide variety of cell surface and secreted proteins. They contribute to many biological processes and diseases (including cancer) as they mediate cell-cell and cell-environment interactions. As such, there has been great interest in mucins. Despite this interest, little is known about their molecular structures and biological activities. This is due to challenges arising from the size, heavy glycosylation and protease resistance of mucins. To overcome these challenges the inventors have identified a new tool- the bacterial protease StcE, that can be used to study the biology of mucins. StcE efficiently and selectively cleaves mucin domains by recognizing a discrete peptide and glycan-based motif. The StcE protease now enables mucins to be selectively liberated from biological samples and cut into fragments amenable to analysis. This technology provides a much-needed tool for the study of mucin domain structure and function.
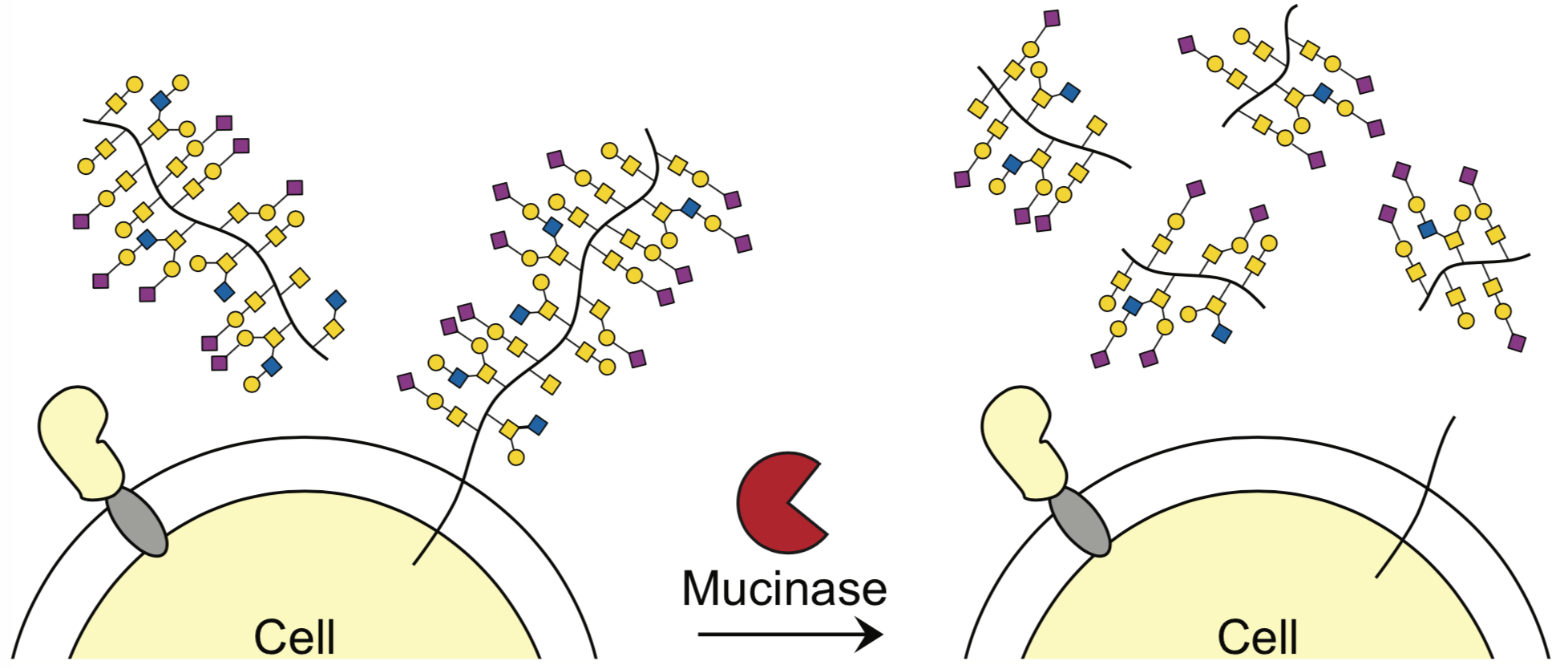
Stage of research
The inventors used StcE to perform molecular and functional analysis of human mucins. Additional development is ongoing.
Applications
- Research tool to study mucin biology:
- Glycoproteome mapping of mucin glycosites and their associated glycoforms
- Selective cleavage, release and enrichment of mucins from cell and tissue materials
- Study native mucin biology
Advantages
- Solves an unmet need- first tool to cleave mucin domains in a peptide and glycan specific manner
- Enables specific release of mucins from biological samples
- Enables analysis of mucin domains by mass spectrometry
- Enables selective depletion, isolation and proteolysis of mucin proteins
- Predictable- active due to defined peptide and glycan-based consensus motif
- Good reagent due to enzyme's:
- Ease of purification- can be purified at scale as a single reagent
- Stability
- Potency
Publications
- Malaker SA, Pedram K, Ferracane MJ, Bensing BA, Krishnan V, Pett C, Yu J, Woods EC, Kramer JR, Westerlind U, Dorigo O, Bertozzi CR. The mucin-selective protease StcE enables molecular and functional analysis of human cancer-associated mucins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Apr 9;116(15):7278-7287
Related Links
Patents
- Published Application: WO2020097386
- Published Application: 20220003777
Similar Technologies
-
PROGRAMMABLE ANTIBODY-BASED MOLECULAR SWITCHES FOR TARGET ANALYTE DETECTION S19-410PROGRAMMABLE ANTIBODY-BASED MOLECULAR SWITCHES FOR TARGET ANALYTE DETECTION
-
ASAP1 and ASAP2: Fluorescent voltage sensor with fast kinetics for imaging high-frequency neuronal electrical activity S13-389ASAP1 and ASAP2: Fluorescent voltage sensor with fast kinetics for imaging high-frequency neuronal electrical activity
-
bReaCh-ES: An optogenetic tool for stimulating neurons with red light S15-285bReaCh-ES: An optogenetic tool for stimulating neurons with red light