Docket #: S23-002
Targeted Molecule Delivery to Microglia through the Blood-Brain Barrier
Researchers at Stanford have facilitated active agent passage across the blood-brain barrier (BBB) by conjugating the active agent with a plasma protein that gets taken up by microglia.
The BBB is a partitioning layer that regulates the passage of substances to protect the brain from potential harm. While its selective permeability is crucial for neural protection, it makes drug delivery to the brain extremely difficult, limiting treatment efficacy for various neurological or psychiatric conditions. It is important to enable the necessary therapeutics to traverse the BBB in order to ensure targeted and efficient delivery to the intended brain region.
Stanford researchers have discovered a brain drug delivery method that capitalizes on a natural transport mechanism. They identified and engineered a drug delivery platform based on a plasma protein called Apolipoprotein A1 (Apo1A1) that can inherently cross the BBB. The ApoA1-conjugated active therapeutic agent crossed the BBB successfully and was found in brain microglia in mice.
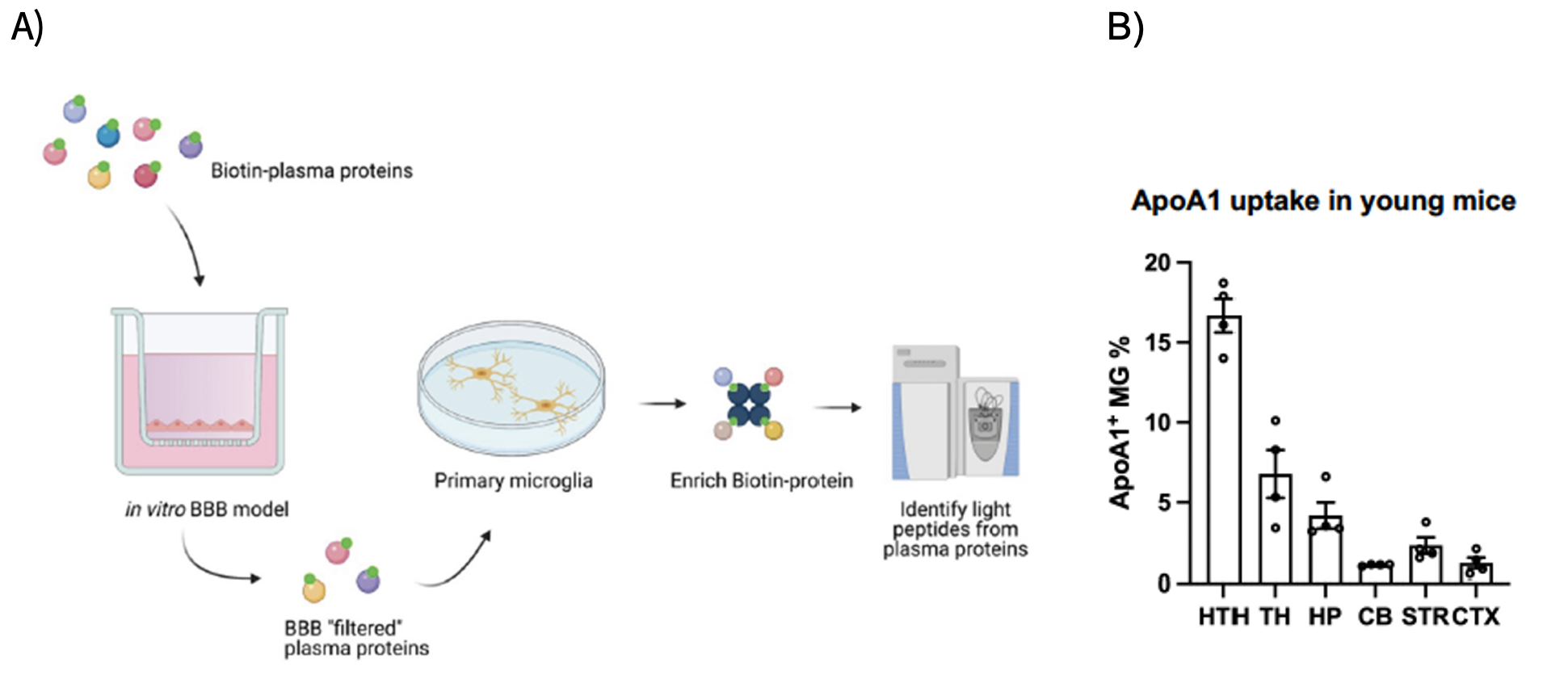
Figure 1. A) Experiment overview. B) Percentage of ApoA1+ microglia (MG) in 6 different brain regions (n = 4).
Stage of Development
In vivo data
Applications
- Brain drug delivery platform for:
- Neurodegenerative diseases
- Brain tumors
- Neurological infection
- Pain management
- Psychiatric disorders
- Trauma
Advantages
- Novel
- Leverages the natural uptake of plasma protein by microglia to cross the BBB
- No alteration of the BBB or immune system required
Related Links
Patents
- Published Application: WO2024158816
Similar Technologies
-
Development of SDF1alpha containing nanoparticles for the treatment of cardiovascular, Neurovascular, and skin impairments S23-446Development of SDF1alpha containing nanoparticles for the treatment of cardiovascular, Neurovascular, and skin impairments
-
Improving the solubility and pharmacokinetic profile of an insoluble therapeutic S22-073Improving the solubility and pharmacokinetic profile of an insoluble therapeutic
-
Bio-engineered mitochondria for targeted delivery to cells, tissue, and organs S24-026Bio-engineered mitochondria for targeted delivery to cells, tissue, and organs