Docket #: S19-253
Targeting Osteopontin: Novel Strategy to Treat Cancer and Inflammation
Researchers at Stanford have developed humanized therapeutic antibodies to treat cancers, particularly melanoma, as well as inflammatory disorders. These patented antibody structures target osteopontin (OPN), a protein that may be cleaved by thrombin and enable immune-modulation, especially in tumors. Blockade of OPN cleavage or blocking of OPN fragments provides a novel approach to regulating cancer progression and survival. Previous studies have implicated OPN in promoting invasive and metastatic progression of many cancers. Leung Lab experimental mouse models indicate that thrombin cleavage of OPN plays a critical role in the growth and progression of B16 melanoma in vivo. These humanized therapeutic antibodies prevent osteopontin cleavage by thrombin and/or block activity of the resulting fragments, and could potentially treat disorders like melanoma, glioblastoma, ovarian cancer, inflammation, cardiac hypertrophy, and myocardial fibrosis.
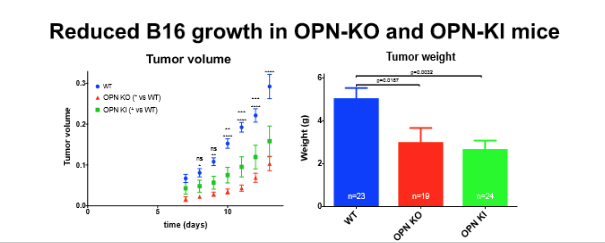
Figure 1- Research Results for B16 growth in OPN-KO and OPN-KI mice: Subcutaneous B16 tumors grew slower on OPN-KO and OPN-KI mice than the wild type, suggesting the effects of OPN deficiency are via thrombin cleavage of OPN. (Image courtesy the Lueng Lab)
Stage of Development – Research In Vivo
Leung Lab mouse studies demonstrate B16 melanoma growth is suppressed in OPN knock-out mice, indicating that targeting OPN cleavage or its fragments represents a promising approach for cancer treatment.
Applications
- Treatment of melanoma and other cancers, either as a monotherapy or in combination
- Treatment of inflammatory disorders, such as cardiac hypertrophy, and myocardial fibrosis
Advantages
- Reduces tumor growth
Publications
- Leung, L. L., Morser, M. J., & Myles, T. (2025). U.S. Patent Application No. 19/229,995.
Related Links
Patents
- Published Application: WO2021030209
- Published Application: 20220324956
- Published Application: 20250361293
- Issued: 12,351,625 (USA)
Similar Technologies
-
Novel systems for inhibiting Neuromedin signaling in vivo S15-356Novel systems for inhibiting Neuromedin signaling in vivo
-
Potent LIF Receptor "Trap" as Cancer Therapeutic S18-098Potent LIF Receptor "Trap" as Cancer Therapeutic
-
Therapeutic Agents Targeting Tumor Associated Macrophages in Obesity S20-321Therapeutic Agents Targeting Tumor Associated Macrophages in Obesity