Docket #: S20-045
High-Efficiency, Low Voltage Stress Power Amplifier with Push-Pull Wave-Shaping Operation
Researchers in the Stanford University Power Electronics Research Lab have designed an easy to implement, high-efficiency, high-frequency power amplifier with low voltage stress. The design uses a combination of circuit stages operating out of phase to provide push-pull operation; a switching circuit and impedance path to drive the circuit; and a waveform-shaping circuit to shape the voltage for presentation to the switching circuit. The SUPER Lab high efficiency amplifier prototype produces higher power than a conventional Class E circuit, reduces voltage stress, has low circulating energy, reduced filtering requirements, and load-independent Zero Voltage Switching operation, making it particularly attractive for energy hungry, high-voltage and high-frequency radiofrequency and microwave applications (e.g. RF plasma generators, cellphone antenna, MRI resonators), wireless charging and more.
Stage of Development – Prototype
The SUPER Lab built and tested a 6.78-MHz 300-W series stacked push–pull ?2 amplifier with a T-network ("PPT ?2" amplifier prototype figure 1) that reached 96% peak total efficiency and high efficiency across a wide range of voltage and power (figure 2). Future performance improvement plans include incorporating recent innovations in wide bandgap (WBG) power semiconductors. Using this amplifier topology, the SUPERLab built and tested a 6.78-MHz 1.7-kW wireless charging system that reached a 95.7% dc-dc efficiency for an electric car, with an ongoing effort of pushing the power beyond 5 kW.
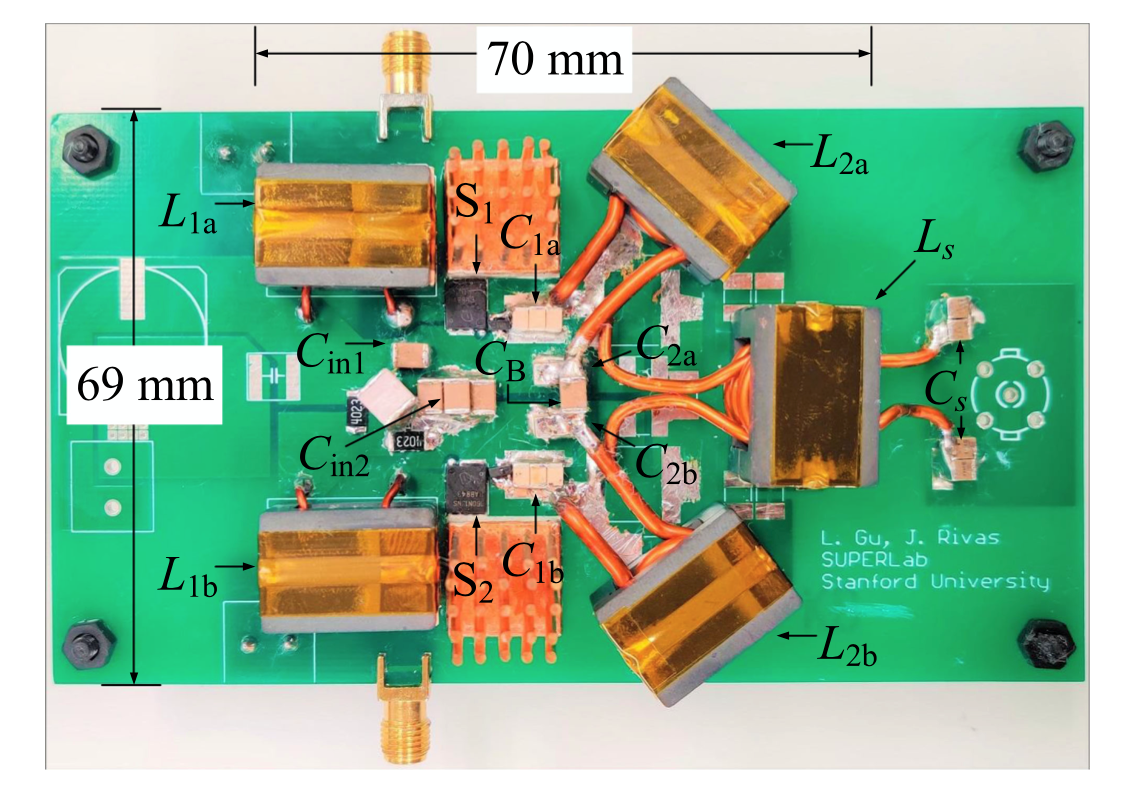
Figure 1 Series-stacked PPT ?2 Prototype
Courtesy SUPER Lab.
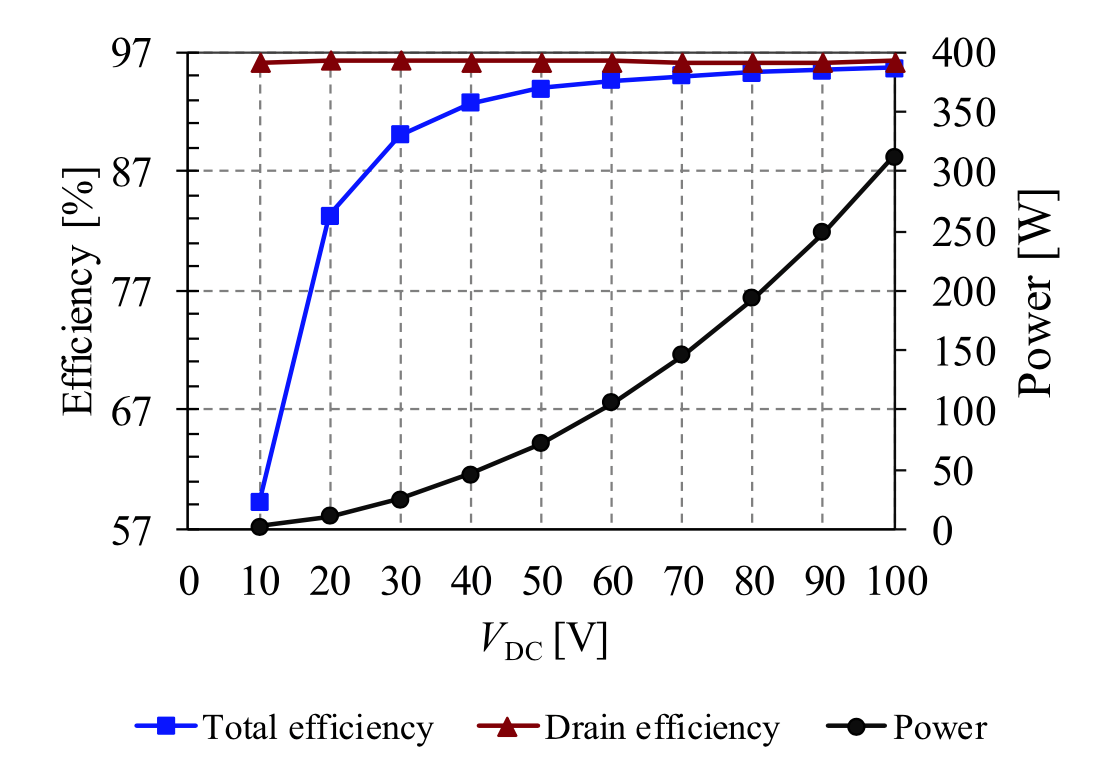
Figure 2 Measured Efficiency vs Input Voltage VDC
Courtesy SUPER Lab.
Applications
- RF power source for plasma loads (Plasma Etch), MRI resonators, amplifiers for cellphones or base stations, transformed-isolated dc-dc power converters.
- Wireless charging for applications ranging from consumer electronics to medical implants, electric vehicles, robots, etc.
Advantages
- Compact and lower cost.
- High energy conversion efficiency leads to higher power capability.
- Compact and simple to implement with reduced filtering requirements.
Publications
- Gu, L., & Rivas-Davila, J. (2021, June). 1.7 kW 6.78 MHz wireless power transfer with air-core coils at 95.7% dc-dc efficiency. In 2021 IEEE Wireless Power Transfer Conference (WPTC) (pp. 1-4). IEEE.
- Gu, Lei, Grayson Zulauf, Aaron Stein, Phyo Aung Kyaw, Tuofei Chen, and Juan Manuel Rivas Davila. "6.78-MHz wireless power transfer with self-resonant coils at 95% DC–DC efficiency." IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics 36, no. 3 (2020): 2456-2460.DOI: 10.1109/TPEL.2020.3014042
- Gu, Lei, Grayson Zulauf, Zhemin Zhang, Sombuddha Chakraborty, and Juan Rivas-Davila. "Push–Pull Class ?2 RF Power Amplifier." IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics 35, no. 10 (2020): 10515-10531. DOI: 10.1109/TPEL.2020.2981312
Related Links
Similar Technologies
-
Wide bandgap (WBG) power semiconductors with reduced gate loss S19-044Wide bandgap (WBG) power semiconductors with reduced gate loss
-
A robust and low-cost tunable matching network S23-224A robust and low-cost tunable matching network
-
Sorting Semiconducting Carbon Nanotubes for Electronic Devices S10-392Sorting Semiconducting Carbon Nanotubes for Electronic Devices