Docket #: S18-437
Simultaneous acquisition of Qualitative and Quantitative MRI (Q2MRI) using deep learning
Stanford researchers at the Xing Lab have developed a novel method using deep neural networks called "Q2MRI" to simultaneously acquire qualitative MR image and quantitative MRI parametric maps without changing the clinical imaging protocol or elongating MRI scan time. Currently, quantitative MRIs are obtained from a series of qualitative MRI, which takes prohibitively long scan times. The new method automatically derives quantitative MRI from a single qualitative MRI with an established prediction model. In addition, the proposed approach suppresses measurement errors caused by RF inhomogeneity and eliminates the possibility of inter-scan motion. This invention will enable broader use of quantitative MRIs which provides more information about tissue characterization and tissue response assessment than qualitative MRIs.
Figure 1

Figure 1 description - Generating quantitative T1 map and proton density map from qualitative T1 weighted MRI (a) using conventional model fitting and (b) using a deep convolutional neural network.
Figure 2
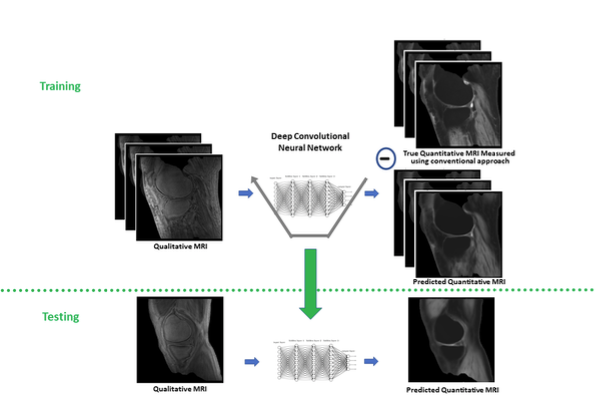
Figure 2 description - Training and testing of a neural network for the derivation of quantitative MRI from a single qualitative MRI. Notice that the ground truth image is obtained using conventional quantitative MRI.
Stage of Research:
Applications
- Quantitative MRI can be used for:
- Characterizing pathology/tumors
- Predicting treatment response
- Diagnosis of diseases with higher specificity than qualitative MRI
- Providing noninvasive surrogate for biopsy in some applications
- Data sharing across different medical centers that prescribe different imaging protocols
- Generating of electron density in MRI-only radiation therapy treatment planning
- Facilitating more accurate and robust segmentation
Advantages
- Simultaneous acquisition of qualitative and quantitative MRIs
- Significant savings in scan time, image processing time, and corresponding costs:
- No extra scan time is required for the derivation of quantitative maps. The only input image is qualitative, obtained for routine clinical purpose.
- Provides data-driven end-to-end mapping from a conventional qualitative MR image to the corresponding quantitative MR parametric maps.
- Suppresses measurement errors caused by RF inhomogeneity.
- Eliminates possibility of inter-scan motions which commonly occur in conventional quantitative MRI between the acquisition of different qualitative images. Image registration is no longer needed.
- Enables broader use of quantitative MRIs
Related Links
Patents
- Published Application: 20210313046
- Issued: 11,948,676 (USA)
Similar Technologies
-
Retrospective Tuning of MR Image Contrast for Precision Imaging S19-233Retrospective Tuning of MR Image Contrast for Precision Imaging
-
A method for tracking moving sources with PET S14-171A method for tracking moving sources with PET
-
Nonrigid Motion Correction Through Autofocusing S12-492Nonrigid Motion Correction Through Autofocusing