Docket #: S16-453
Efficient homologous recombination of large transgenes using AAV donor vectors
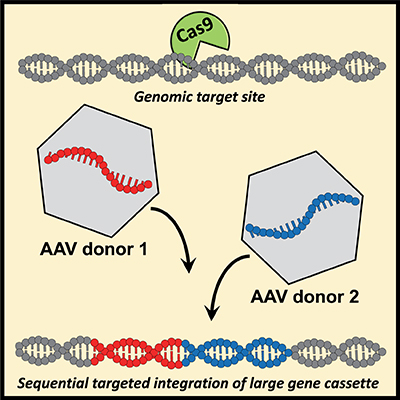
Researchers at Stanford have developed methods to overcome the limited packaging capacity of adeno-associated virus (AAV) vectors and enable their use in integration of large transgenes. AAV vectors can transduce dividing and non-dividing cells and have been used as vectors for homologous recombination in vitro and in vivo. However, AAV vectors have a maximum packaging capacity of approximately 4.5kb. With the required homology arms this leaves approximately 3.7kb for a transgene expression cassette, which limits the use of AAV donor vectors in genome editing applications. To overcome this limitation the inventors have developed a method to integrate large transgenes by using two donor AAV vectors. These vectors undergo sequential homologous recombination stimulated by CRISPR/Cas9 to integrate large DNA that exceeds the packing capacity of a single AAV vector. This technology provides an effective solution to enable more widespread use of AAV vectors in genome editing, including in therapeutic applications.

Stage of research
This method has been used in primary human T cells and CD34+ hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells to successfully, site-specifically integrate a 5.7kb transgene expression cassette.
Figure adapted from: Bak, R. O., and Matthew H. Porteus. "CRISPR-Mediated Integration of Large Gene Cassettes Using AAV Donor Vectors." Cell Reports (2017). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2017.06.064 .4297
Applications
- Genome editing
- Gene therapy - treat genetic diseases involving mutations in large genes such as:
- Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (dystrophin: 11kb)
- Hemophilia A (Factor VIII: 7kb)
- Cystic Fibrosis (CFTR: 4.4kb)
- Cell engineering - use multicistronic expression cassettes to express multiple proteins from the same cassette
Advantages
- Solves an unmet need - enables targeted integration of large transgenes (bigger than 4kb) using AAV vectors
- First successful use of homologous recombination and 2 donor vectors to integrate large DNA
- Single step procedure - does not require serial transfection and transduction of cells
Publications
- Bak, R. O., and Matthew H. Porteus. "CRISPR-Mediated Integration of Large Gene Cassettes Using AAV Donor Vectors." Cell Reports, 20, 750-756. 18 July 2017.
Related Links
Patents
- Published Application: WO2018195555
- Published Application: 20200131539
- Issued: 11,773,409 (USA)
Similar Technologies
-
A multiplexed RNA regulation platform for primary immune cell engineering S22-235A multiplexed RNA regulation platform for primary immune cell engineering
-
Robust factor IX minigene expression cassette (TTR) S06-099Robust factor IX minigene expression cassette (TTR)
-
MAGESTIC - A High Efficiency, Massively Parallel Production of Genetically Engineered Clones for Functional Genomics and Synthetic Biology S17-020MAGESTIC - A High Efficiency, Massively Parallel Production of Genetically Engineered Clones for Functional Genomics and Synthetic Biology