Docket #: S19-193
Compact, Parallel, High-Fidelity 7-DOF Haptic Device
Researchers in the Stanford Robotics Lab have developed a compact high-fidelity haptic teleoperation system which shows accurate and isotropic behavior in translation and rotation. Its new 7-degree-of-freedom cable-driven paired parallel architecture provides precise motion with low inertia, minimal joint clearance and minimal friction in freespace, and excellent force feedback within a large stiffness bandwidth while in contact. The device is compact, lightweight, and portable, making it easy to integrate in any workstation. An ergonomic actuated gripper, integrated inside the handle, provides an additional grasping degree of freedom and fingertip force feedback. Paired with the workspace mapping controller (see Stanford docket S19-192),the system motions and forces are imperceptibly drifted and scaled to deliver precise remote control and high perception in any environment, making it attractive for a range of applications including medical and surgical robotics, and telerobotics in hazardous environments.
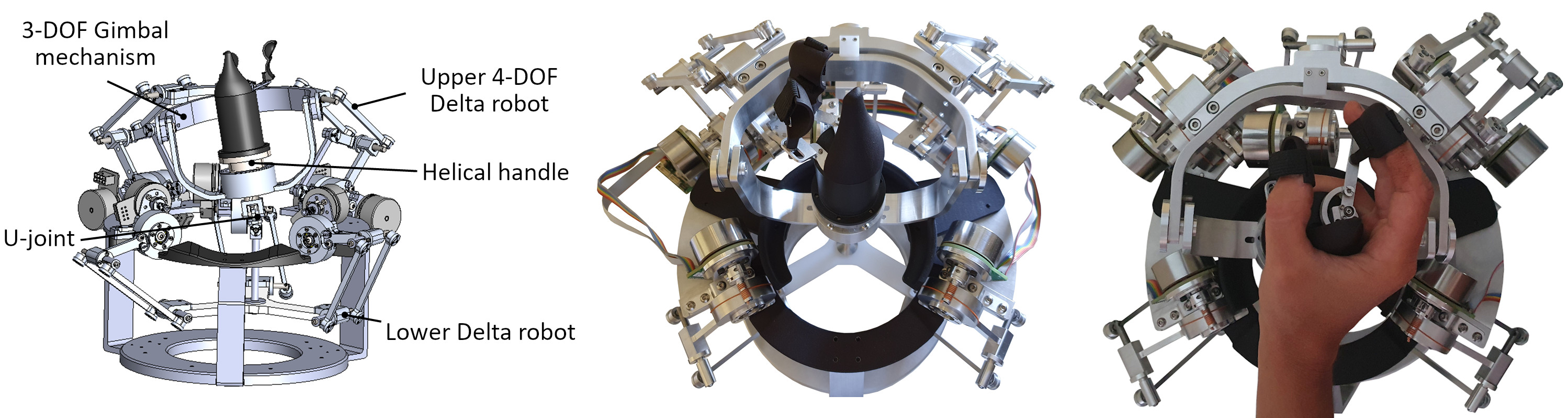
Compact and High-Fidelity Device for Versatile Haptic Teleoperation The mechanical transparency of the design and its novel paired parallel structure meet the challenge of accuracy, stiffness, and haptic capability required in remote tasks. Image courtesy The Stanford Robotics Lab
Stage of Development – Prototype
The Stanford Robotics Lab researchers are using the high-fidelity haptic device with their workspace mapping controller in industrial applications and underwater explorations. Research is ongoing.
Applications
- Medical & surgical robotics
- Telerobotics for hazardous environments (aerospace, underwater, nuclear, polluted, industrial operations)
- Cobots, and Industry 4.0 (I4.0) technologies for the smart factory
- Virtual / Augmented Reality and interactive simulations
Advantages
- Transparent and imperceptible to user – precise motion control in an unconstrained and free space without reaching workspace limits.
- Intuitive, compact and ergonomic with accurate force feedback to perceive the remote environment.
- Versatile and suitable for different applications and user preferences.
Related Links
Similar Technologies
-
Drift-based Adaptive Workspace Mapping Controller for Haptic Interaction S19-192Drift-based Adaptive Workspace Mapping Controller for Haptic Interaction
-
Haptic Interface with Variable Stiffness and Deformable Geometry S12-428Haptic Interface with Variable Stiffness and Deformable Geometry
-
Device to retract soft growing robots S19-431Device to retract soft growing robots