Docket #: S11-298
Chimeric AAV Capsids for High Efficiency Nucleic Acid Transfer
Researchers in Prof. Mark Kay's laboratory have developed recombinant adeno-associated viral (AAV) capsid proteins that transduce human primary hepatocytes at high efficiency in vitro and in vivo. This vector (AAV-LK03) was engineered through a unique protocol of DNA shuffling and selection using a humanized murine model. This method facilitated the final selection of a vector that is capable of highly efficient functional transduction, leading to a high level of transgene expression. The AAV-LK03 vector is a highly promising clinical candidate for gene therapy applications and could also be used for research that requires genetic manipulation of xenotransplanted cells.
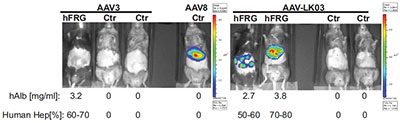
AAV-LK03 is selective for human hepatocytes in vivo. The newly engineered AAV chimera (AAV-LK03) selectively transduced human hepatocytes (in humanized FRG animals – hFRG) but not in non-humanized controls (Ctr). Conversely, the AAV3 vector did not transduce either type of mouse and the AAV8 vector was not specific for human hepatocytes (as shown by transduction of the Ctr mouse). Human albumin (hAlb) levels and estimated percentages of repopulation with human hepatocytes are given for each animal.
Stage of Research
The inventors have engineered the chimeric AAV vector and demonstrated its efficacy in vitro and in vivo (43% mean transduction in human hepatocytes).
Applications
- Gene transfer in vitro and in vivo, with end user applications in:
- therapeutics - gene therapy
- research - genome editing, gene modification in mouse models of human diseases
- specific transduction of human xenotransplant models
Advantages
- High efficiency - mean in vivo transduction of 43% in mouse graft of human hepatocytes (compared to 4% for conventional AAV8 vectors)
- Specific - vectors designed for high efficiency in hepatocytes
- Low immunogenicity - low level of neutralization by human immune system
Publications
- Melo, Sandra P, Leszek Lisowski, Elizaveta Bashkirova, Hanson H Zhen, Kirk Chu, Douglas R Keene, M Peter Marinkovich, Mark A Kay, and Anthony E Oro. "Somatic Correction of Junctional Epidermolysis Bullosa by a Highly Recombinogenic AAV Variant." Mol Ther Molecular Therapy, 2014, 725-33.
- Lisowski L, Dane AP, Chu K, Zhang Y, Cunningham SC, Wilson EM, Nygaard S, Grompe M, Alexander IE, Kay MA, "Selection and evaluation of clinically relevant AAV variants in a xenograft liver model." Nature. 2013 Dec 25.
Patents
- Published Application: 20130059732
- Published Application: WO2013029030
- Published Application: 20150376607
- Published Application: 20180258420
- Published Application: 20210355481
- Issued: 9,169,299 (USA)
- Issued: 9,856,469 (USA)
- Issued: 11,015,189 (USA)
- Issued: 12,534,717 (USA)
Similar Technologies
-
Antiviral CRISPR Systems for Modulating Host Immune Response and Targeting the Virus Genome S20-082Antiviral CRISPR Systems for Modulating Host Immune Response and Targeting the Virus Genome
-
Gene therapy for optic neuropathies S19-014Gene therapy for optic neuropathies
-
Treatment of dilated cardiomyopathy and other disorders characterized by systolic heart failure with ATF4 gene therapy S23-405Treatment of dilated cardiomyopathy and other disorders characterized by systolic heart failure with ATF4 gene therapy