Docket #: S23-369
Diode-pumped photonic integrated titanium-sapphire waveguide amplifier
Stanford researchers have developed ultra-wideband amplification of near infrared signals for the first time on a photonic integrated circuit. Previously, optical amplification on photonic integrated circuits has been limited to wavelengths longer than 1000 nm, which has restricted use in biological applications. Furthermore, tabletop titanium-sapphire are large, cost, and require high optical pump powers. The Stanford developed diode-pumped photonic integrated titanium-sapphire waveguide amplifier incorporates the critical near-infrared window for biological tissue, which is pivotal for medical imaging and diagnostic equipment, as well as provides an on-chip solution for applications such as quantum technology, LiDAR and beyond.
The device consists of a nanophotonic crystalline thin-film titanium-sapphire optical waveguide co-integrated with a semiconductor diode-laser used to pump the titanium-sapphire waveguide. The nanophotonic titanium sapphire waveguide amplifies optical signals with wavelength ranging from 700 nm to 1000 nm. The titanium-sapphire waveguides do not absorb when the material is not pumped, and passive propagation losses are smaller than 0.45 dB/cm. These titanium-sapphire waveguides outperform currently available optical gain waveguides, and meets the needs of a wide range of applications in photonic integrated circuits
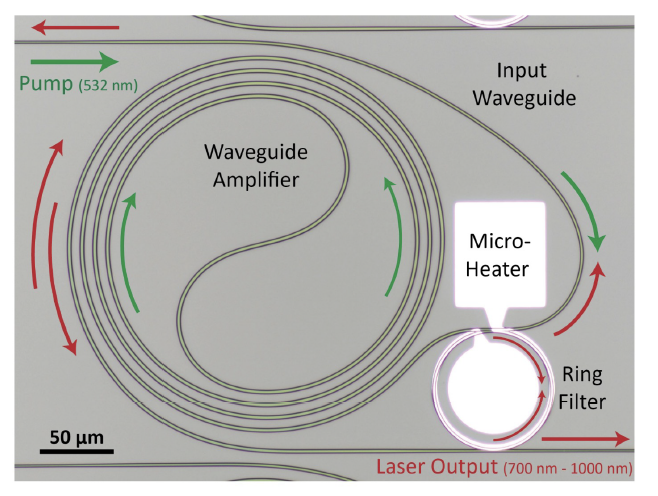
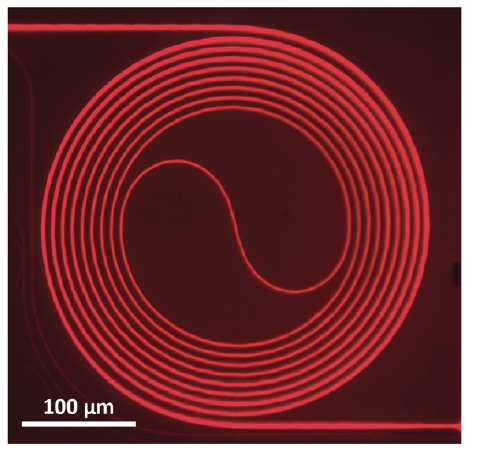
Ti:Sapphire waveguide amplifier as stand-a-lone chip optical amplifier (Top) and
Ti:Sapphire waveguide amplifier prototype (Bottom)
(Image courtesy the Nanoscale and Quantum Photonics Lab)
Stage of Development – Proof of Concept Prototype
Applications
- On chip, high performance, ultra-wideband lasers and amplifiers for:
- Quantum computing, simulations, sensing, and networks
- Data communications
- Positioning, navigation, and timing (PNT) systems
- LiDAR
- Augmented and virtual reality
- Biomedical applications, such as optical coherence tomography (OCT), medical devices, proton therapy, microscopy, spectroscopy, imaging, surgery, etc.
Advantages
- Compact, photonic integrated circuit
- First time, ultra-wideband amplification of near infrared signals on a photonic integrated circuit
- Lower cost than existing table-top systems
Publications
- Myers, A. (2024, June 26). Chip-scale titanium-sapphire laser puts powerful technology in reach. Stanford News. https://news.stanford.edu/stories/2024/06/a-chip-scale-titanium-sapphire-laser
- Yang, J., Van Gasse, K., Lukin, D. M., Guidry, M. A., Ahn, G. H., White, A. D., & Vu?kovi?, J. (2024). Titanium: sapphire-on-insulator integrated lasers and amplifiers. Nature, 630(8018), 853-859.
Related Links
Patents
- Published Application: WO2025085856
Similar Technologies
-
Breakthrough Optical Frequency Processing for Quantum Computing and Beyond S24-365Breakthrough Optical Frequency Processing for Quantum Computing and Beyond
-
Light sheet fluorescence microscopy using high speed structured and pivoting illumination S16-332Light sheet fluorescence microscopy using high speed structured and pivoting illumination
-
Photon spin processor for on-chip classical and quantum information systems S24-212Photon spin processor for on-chip classical and quantum information systems