Docket #: S18-432
Enhanced Transplantation of Pancreatic Islets via Controlled Nutrient Delivery System
Background:
In type 1 diabetes, donor islets are used to replace those destroyed by autoimmunity as a potentially curative therapy for this chronic disease. However, transplanted islets encounter difficulty during engraftment, and suffer from fatal nutrient shortages before they are able to become vascularized within host tissue.
Technology:
Researchers at Stanford have developed a nanoparticle system that can support donor islets with a controlled and sustained supply of nutrients until they are able to establish their own supply over time Mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSNP) are loaded with glutamine, which an amino acid that serve as a vital nutrient and energy source for donated islets post-transplantation; the glutamine-loaded MSNPs are then coated with polydopamine to enable the slow release of this nutrient supply over a 14 day period. Islets transplanted with glutamine-loaded, polydopamine-coated MSNPs enjoy a longer lifespan in vitro and in vivo, enabling insulin production in animal models of Type 1 diabetes. Not only can the cargo within MSNPs be substituted for other nutrients (i.e. other amino acids, carbohydrates, etc), the platform can also be used for to support other cellular therapies both in vitro and in vivo.
Results
In vitro
The inventors optimized the concentration and incubation periods for glutamine and polydopamine with MSPNs that best support supported islet survival. These islets showed significantly greater survival and increased insulin secretion relative to control cells.
In vivo
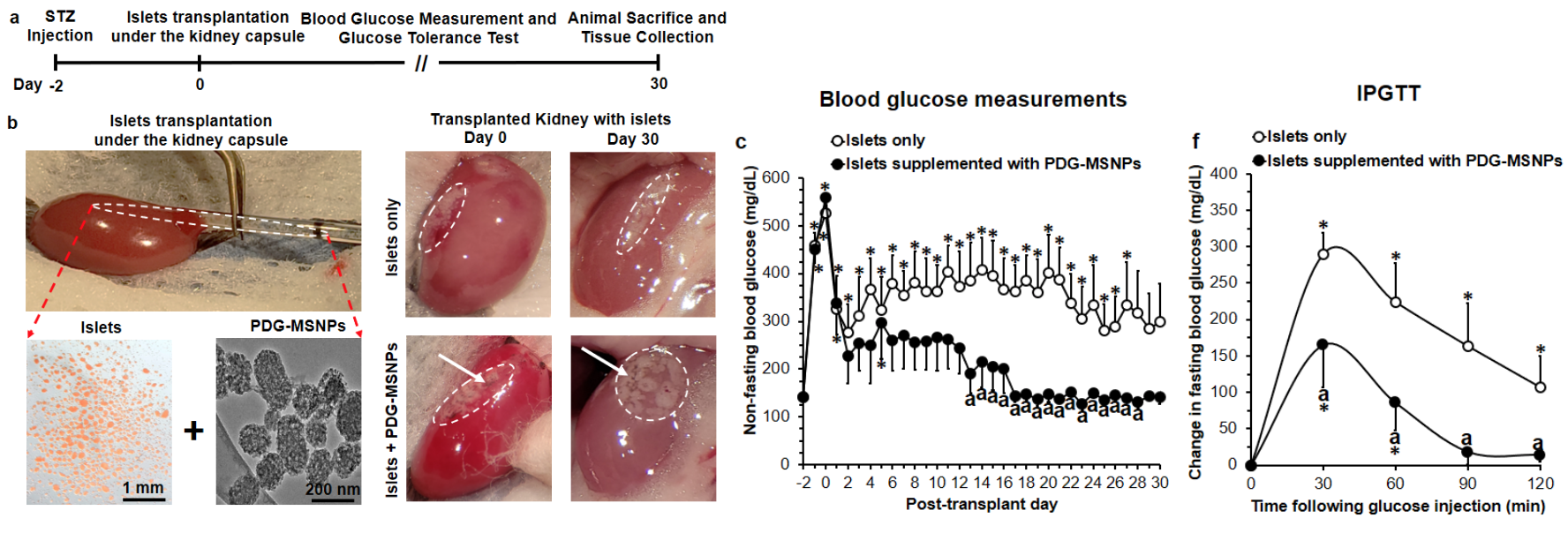
In a mouse model of Type 1 diabetes, pancreatic islets transplanted with polydopamine-coated, glutamine-loaded MSNPs induced a return to normal glucose control, while control islets alone produced only a transient period of normoglycemia. Glucose control was maintained in animals for at least one month, and these nanoparticles were able to exist at their site of implantation with no signs of immune response or fibrosis after six months.
Applications
- Tissue transplantation
- Type 1 diabetes cell therapy
- Biomaterials for regenerative medicine
- Nutrient support for isolated cell systems
Advantages
- Increased longevity of transplanted islets resulting in improved islet transplantation
- Potential reduction in islet number for transplantation (or stem cell derived beta cells)
- Optimized, sustained release nutrient delivery platform with interchangeable cargo and release profile that can be modulated to match requirements
Patents
- Published Application: WO2021055575
- Published Application: 20220401397
- Issued: 12,558,334 (USA)
Similar Technologies
-
hPSC culture for differentiating blood, cardiomyocytes, and other mesoderm cells S14-259hPSC culture for differentiating blood, cardiomyocytes, and other mesoderm cells
-
Use of Focal Adhesion Kinase Inhibitors To Improve the Quality and Appearance of Split Thickness Skin Grafts S20-006Use of Focal Adhesion Kinase Inhibitors To Improve the Quality and Appearance of Split Thickness Skin Grafts
-
Biomarker to Enrich for Inflammation-Resistant Cartilage to Treat Osteoarthritis S16-017Biomarker to Enrich for Inflammation-Resistant Cartilage to Treat Osteoarthritis