Docket #: S07-120
Laser-driven deflection structure for charged particle beams
Researchers in the Ginzton lab at Stanford University have patented an all-dielectric laser-driven microstructure for producing controllable charged particle beam. The key concept for this laser-driven undulator is its ability to provide phase synchronicity between the deflection force from the laser and the electron beam for a distance that is much greater than the laser wavelength. Because of the possibility of high-peak electric fields from ultrashort pulse lasers on dielectric materials, the proposed undulator is expected to produce phase-synchronous GV/m deflection fields on a relativistic electron bunch and therefore lead to a very compact free electron-based radiation device. End user applications include particle accelerators, security scanners, and X-rays for medical imaging.
Figure
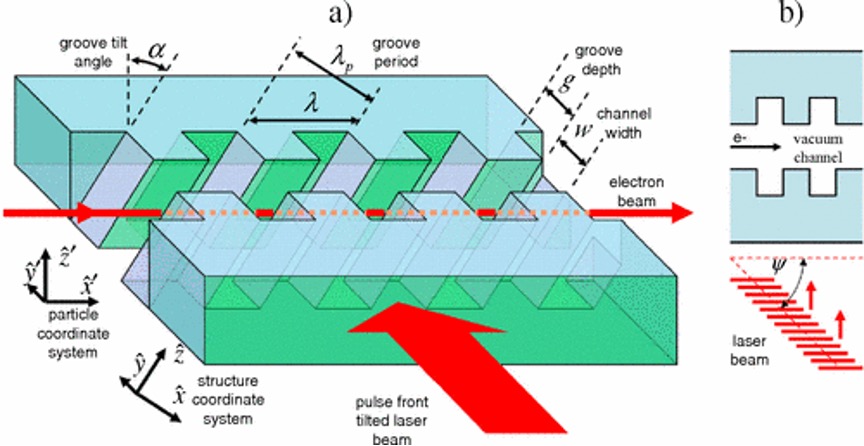
Image credit - Physical Review Special Topics-Accelerators and Beams, Vol. 11, Issue 3, March 20, 2008.
Figure Description- (a) Perspective view of a section of the proposed deflection structure element. (b) Top view of a section of the structure. While the periodic grooves maintain phase synchronicity, the laser pulse-front tilt guarantees synchronicity of the laser pulse envelope with the relativistic electron bunch traveling in the vacuum channel.
Applications
- Dielectric-based laser-driven particle accelerators
- Hd Ultrafast beam switching devices
- Tabletop attosecond streak cameras
- Ultra-short (few-cm) undulators
- Coherent UV or X-rays
- Compact isotope detectors
- End user applications include but are not limited to: security scanners, medical therapy, and X-ray light sources for biological and materials research
Advantages
- Low-cost fabrication with high-strength dielectric materials
- Sustains very high deflection forces
- Reduced alignment issues
- Rapid switching down to femtoseconds and possible GHz repetition rate
Publications
- R. Joel England, Peter Hommelhoff, Robert L. Byer; Microchip accelerators. Physics Today 1 August 2021; 74 (8): 42–49.
- T. Plettner, R.L. Byer, Proposed Tabletop Laser-driven Coherent X-ray Source. Proceedings of PAC07, Albuquerque, NM.
- T. Plettner, R.L. Byer, Proposed Tabletop Laser-driven Coherent X-ray Source. Proceedings of PAC07, Albuquerque, NM.
- T. Plettner, R.L. Byer, Proposed dielectric-based microstructure laser-driven undulator. Physical Review Special Topics-Accelerators and Beams, Vol. 11, Issue 3, March 20, 2008.
Related Links
Patents
- Published Application: 20090314949
Similar Technologies
-
Piezoelectric Neutron Generator (SPAN) S15-084Piezoelectric Neutron Generator (SPAN)
-
Light sheet fluorescence microscopy using high speed structured and pivoting illumination S16-332Light sheet fluorescence microscopy using high speed structured and pivoting illumination
-
Photo Emitter X-Ray Source Array (PeXSA) S12-318Photo Emitter X-Ray Source Array (PeXSA)