Docket #: S18-506
Machine Learning Model for Dose Volume Histograms (DVHs) and Dose Prediction based on Dosimetric Features
Stanford researchers at the Xing Lab have developed a dosimetric features driven- machine learning model for dose volume histograms (DVHs) and dose prediction for volumetric modulated arc therapy (VMAT) planning. This model is an efficient and robust solution to determine optimized radiation dosage for cancer patients using the patient's dosimetric features as input. As compared to the current complicated geometric/anatomical features?based approaches, this invention will be more simple, accurate, and cost-effective.
A validation study showed the accuracy and effectiveness of this model, indicating its great potential in clinical applications for improved planning and quality control. Additionally, this technique can be applied to other disease sites or radiation therapy modalities, such as head and neck, and lung VMAT, Gamma Knife, stereotactic radiosurgery, and other variants of Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT).
Figure:
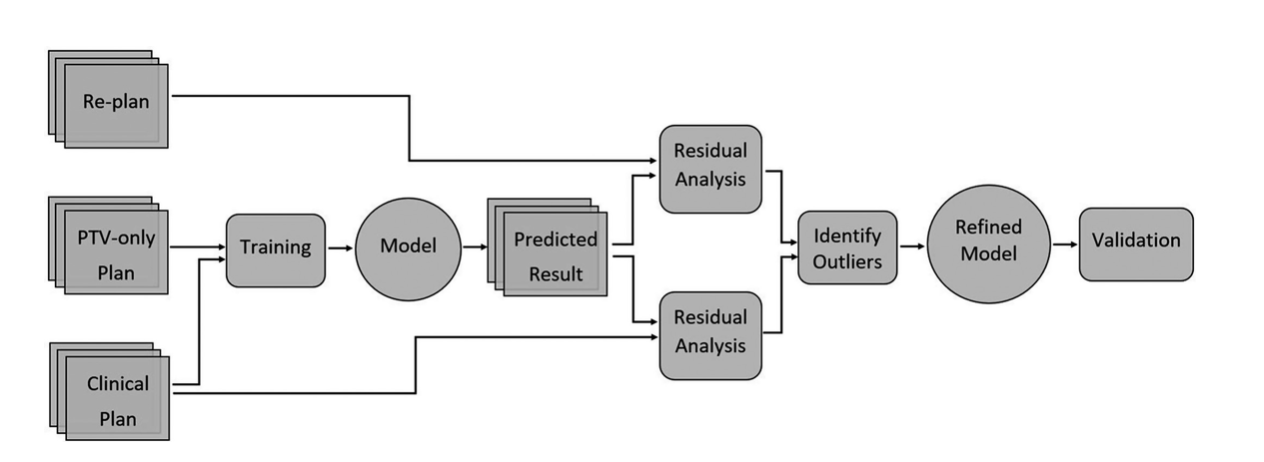
Figure Description:Pipeline of the proposed method.
Stage of Research:
Applications
- Radiation Oncology:
- DVHs/dose prediction for VMAT planning
- The predicted DVHs/dose can be used in knowledge-based and automated planning under the guidance of prior data
- The predicted DVHs/dose can also be used to evaluate treatment plans to ensure a high plan quality
Advantages
- Robust and efficient solution for DVHs/dose prediction in treatment planning and quality assurance (QA)
- Customized - Dosimetric features of the patient is used as model inputs
- Automated - Uses machine learning
- Time and cost savings
- Better patient outcomes
- Can be applied to other disease sites or radiation therapy modalities, such as head and neck, and lung VMAT, Gamma Knife, stereotactic radiosurgery, and other variants of IMRT, including static field and helical IMRT
Publications
- Ma, Ming, Nataliya Kovalchuk, Mark K. Buyyounouski, Lei Xing, and Yong Yang. "Dosimetric features?driven machine learning model for DVH prediction in VMAT treatment planning." Medical Physics (2018).
Related Links
Patents
- Published Application: 20200171325
- Issued: 11,806,551 (USA)
Similar Technologies
-
Deep Learning for In Vivo Near-Infrared Imaging S20-378Deep Learning for In Vivo Near-Infrared Imaging
-
Automated coronary artery calcification (CAC) scoring S20-124Automated coronary artery calcification (CAC) scoring
-
Automated Gait Analysis using video S18-010Automated Gait Analysis using video