Docket #: S14-171
A method for tracking moving sources with PET
Stanford physical oncology researchers have developed a patented trajectory reconstruction method for tracking moving sources labeled with positron-emitting radionuclides using Positron Emission Tomography. The technique reconstructs the time-varying position of individual sources directly from raw list-mode data, bypassing conventional image reconstruction entirely. The Pratx lab studies how cells navigate the body's circulatory system using this non-invasive method. Applications include tracking of single cells in vivo, real-time tracking of a moving tumor during radiotherapy, understanding the efficacy of cell-based therapies, and estimation of respiratory breathing in 4D-PET.
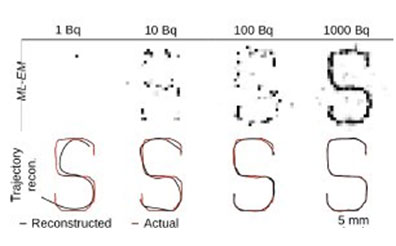
(Image courtesy the Pratx Lab)
Figure 1 Single-source tracking. List-mode PET data from a point source (1, 10, 100, 1000 Bq) moving at 5 mm/s in an S-like pattern was reconstructed using a standard PET Maximum Likelihood Expectation Maximization reconstruction algorithm (top row) and the novel trajectory reconstruction method (bottom row). Results indicate the invention can track a moving source better than can be achieved using conventional MLEM.
Stage of Research
This algorithm can track a single cell inside a small-animal PET system with 2 mm accuracy provided that the activity of the cell (Bq) is greater than twice the square of its velocity (cm/s).
The Pratx Lab uses this approach to study metastasis in vivo, grow and image tumor models in the lab, enhance radiation treatments, and develop additional methods for tracking moving cells anywhere in the body of living subjects.
Applications
- In vivo cell tracking:
- Cell-based therapies for cardiac and neural tissue regeneration and cancer immunotherapy
- Preclinical research tool to study biological processes such as cancer metastasis
- Small animal research for drug development
- 4D PET/CT imaging – estimation of respiratory breathing
- Radiation Therapy - real time tracking of a moving tumor
Advantages
- Real time
- Accurate – can track moving sources with higher localization accuracy and up to higher velocities and lower activities
- •First proposed method -to reconstruct the motion of a source directly from PET. measurements without forming an image – i.e. to track the motion of a single cell in a living organism or hot target (e.g. tumor, etc.) in real time.
Publications
- Nguyen, H. T., Das, N., Ricks, M., Zhong, X., Takematsu, E., Wang, Y., ... & Pratx, G. (2024). ,a href="https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.adk5747">Ultrasensitive and multiplexed tracking of single cells using whole-body PET/CT. Science Advances, 10(24), eadk5747. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adk5747
- Jung, K. O., Kim, T. J., Yu, J. H., Rhee, S., Zhao, W., Ha, B., ... & Pratx, G. (2020). Whole-body tracking of single cells via positron emission tomography. Nature biomedical engineering, 4(8), 835-844.
- Ouyang, Y., Kim, T. J., & Pratx, G. (2016). Evaluation of a BGO-based PET system for single-cell tracking performance by simulation and phantom studies. Molecular imaging, 15, 1536012116646489.
- Lee, K. S., Kim, T. J., & Pratx, G. (2014). Single-cell tracking with PET using a novel trajectory reconstruction algorithm. IEEE transactions on medical imaging, 34(4), 994-1003.
Patents
- Published Application: 20150355347
- Issued: 9,962,136 (USA)
Similar Technologies
-
Deep learning model for 3D computed tomography (CT) image reconstruction with single or a few views S18-464Deep learning model for 3D computed tomography (CT) image reconstruction with single or a few views
-
A novel integrated quality assurance phantom for radiographic and non-radiographic radiotherapy localization and positioning systems S17-451A novel integrated quality assurance phantom for radiographic and non-radiographic radiotherapy localization and positioning systems
-
Deferoxamine prophylaxis for radiation-induced fibrosis S19-455Deferoxamine prophylaxis for radiation-induced fibrosis