Docket #: S19-020
MARIA-Neural network for accurate prediction of HLA class II antigen presentation
The presentation of antigens by Human Leukocyte Antigen (HLA) class II molecules is an essential component of adaptive immune responses. Prediction of which antigen fragments are likely to be presented by class II molecules is of great value for vaccine development and cancer immunotherapies. However, current computational methods trained on in vitro binding data have limitations for accurately predicting class II antigen presentation.
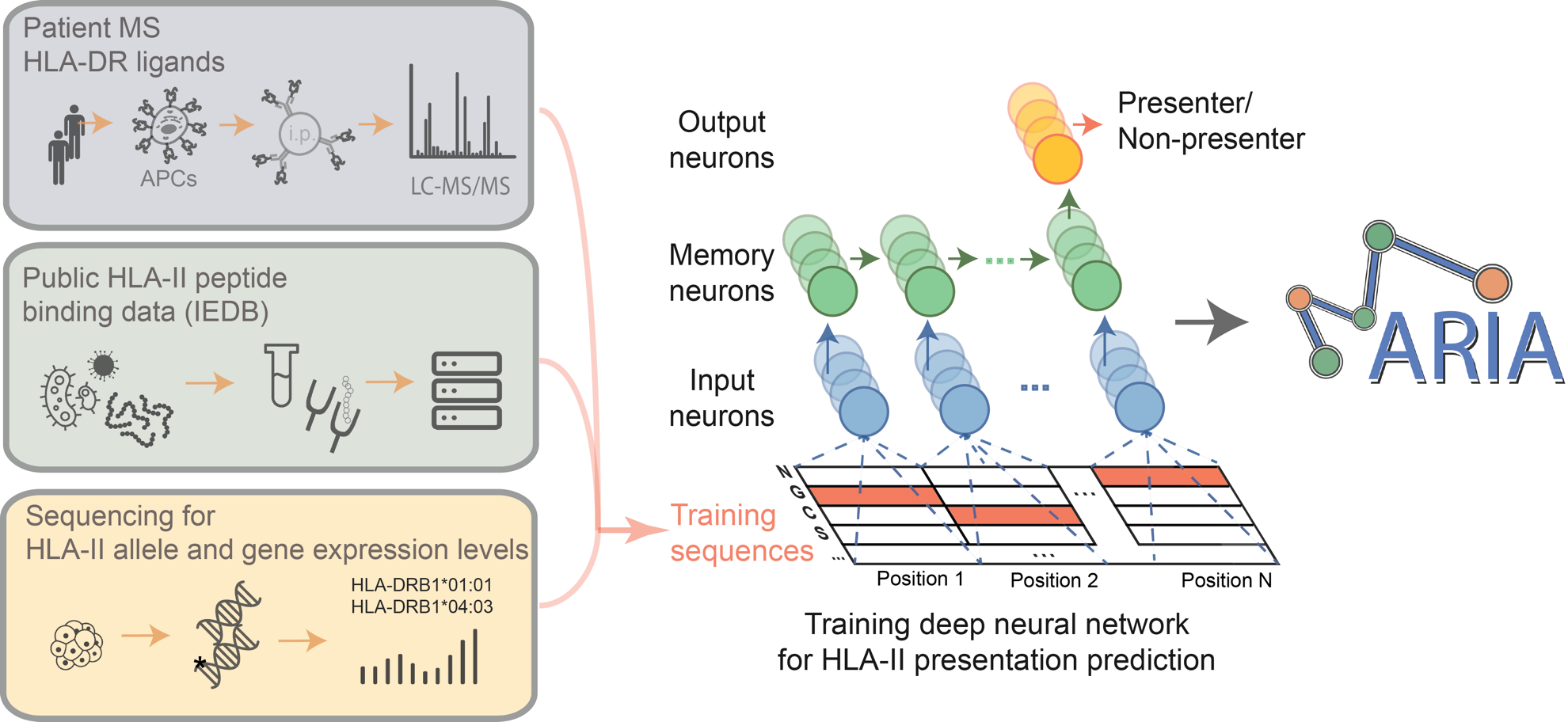
This invention called MARIA, is a deep learning model which predicts HLA class II antigen presentations with higher accuracy. The model learns from in vitro binding measurements, HLA ligand sequences recovered by mass spectrometry, along with gene expression levels, and protease cleavage signatures. The team observed that sequences of empirically recovered of class II ligands to be most informative for prediction. In independent test sets, MARIA outperformed existing methods (AUC=0.89) and allowed identification of immunogenic epitopes in lymphomas, melanomas and celiac disease.
Stage of Development
- Working python package and web-based interface
- Experimentally validated
- MARIA can better identify presented HLA-II antigens and CD4 T-cell epitopes than conventional tools trained on in vitro binding affinities
- Working prototype of MARIA for HLA-I
Applications
- Prediction of presentation of peptides
- Vaccine development (e.g. COVID-19)
- Immune response detection
Advantages
- Higher accuracy than current computational models
- Utilizes machine learning neural network to overcome many challenges of the current state-of-the-art through 3 methods; what it learned from, how it learned it and what kinds of features it considers
- Versatile – MARIA can be trained with all types of data
Publications
- Chen, Binbin, Michael S. Khodadoust, Niclas Olsson, Lisa E. Wagar, Ethan Fast, Chih Long Liu, Yagmur Muftuoglu et al. Predicting HLA class II antigen presentation through integrated deep learning Nature biotechnology 37, no. 11 (2019): 1332-1343.
- Kathuria, K.R., Chen, B., Khodadoust, M.S., Olsson, N., Davis, M.M., Elias, J.E., Levy, R., Altman, R.B. and Alizadeh, A.A., 2019. "Maria-I: A Deep-Learning Approach for Accurate Prediction of MHC Class I Tumor Neoantigen Presentation.
Related Links
Patents
- Published Application: 20210033608
Similar Technologies
-
TLR7-agonist-nanoparticle vaccine adjuvant S21-063TLR7-agonist-nanoparticle vaccine adjuvant
-
Antiviral CRISPR Systems for Modulating Host Immune Response and Targeting the Virus Genome S20-082Antiviral CRISPR Systems for Modulating Host Immune Response and Targeting the Virus Genome
-
System biological analysis of vaccination for mechanisms of adjuvanticity and antibody durability in humans S21-012System biological analysis of vaccination for mechanisms of adjuvanticity and antibody durability in humans