Docket #: S21-448
Metal catalysts in tandem with carbon-based catalysts for CO2 conversion to carbon-based molecules
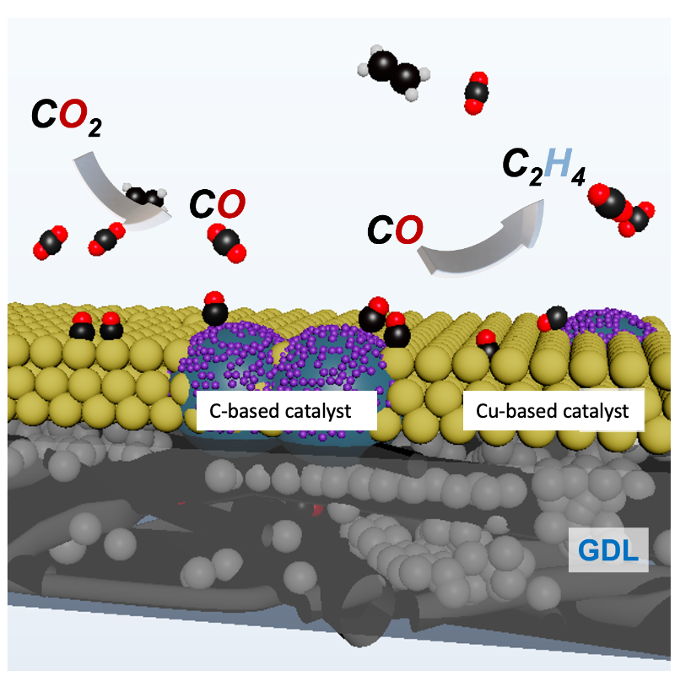
Stanford researchers have developed a novel electrode composed of copper-based catalyst and a carbon-based catalyst to directly convert CO2 into ethylene, a valuable carbon-based molecule. Ethylene (C2H4) is particularly attractive due to its major importance as a feedstock chemical for various applications.
The electrocatalyst is composed of copper-based material and a carbon-based catalyst which enables the formation of CO from CO2. The two materials are integrated into gas diffusion electrodes for direct conversion of vapor-fed CO2 into ethylene. The carbon-based catalyst converts CO2 to CO, and the copper surface converts CO to ethylene. The tandem electrocatalyst enables the high selectivity and formation rate of ethylene on a practical scale, achieving 40% faradaic efficiency (FE) at 150 mA cm-2 and 3.2 V in a membrane electrode assembly electrolyzer. The catalytic performance of the tandem catalysts shows higher energy conversion and lower working voltages compared to any catalyst previously reported. Moreover, this strategy applied towards other catalyst-electrode geometries could be broadly applicable towards reactions for accessing other valuable carbon-based molecules from CO2 like ethanol, acetate, etc.
Figure:
Stage of Development
Prototype
Applications
- Development of catalysts to convert CO2 to valuable carbon-based molecules like ethylene
- By tuning catalyst composition or morphology, can expand to other reactions to access other valuable carbon-based molecules
Advantages
- Mild condition
- High conversion efficiency and ethylene selectivity
- Implementable on practical scale
- Best performance yet for direct conversion of CO2 to ethylene
- 40% faradaic efficiency (FE) at 150 mA cm-2 and 3.2 V in a membrane electrode assembly electrolyzer
Publications
- Lin, Y. R., Lee, D. U., Tan, S., Koshy, D. M., Lin, T. Y., Wang, L., ... & Jaramillo, T. F. (2022). Vapor?Fed Electrolyzers for Carbon Dioxide Reduction Using Tandem Electrocatalysts: Cuprous Oxide Coupled with Nickel?Coordinated Nitrogen?Doped Carbon. Advanced Functional Materials, 2113252.
Related Links
Patents
- Published Application: WO2023177710
- Published Application: 20250161926
Similar Technologies
-
Infrared Spectroscopy of Carbon Dioxide Hydration S21-245Infrared Spectroscopy of Carbon Dioxide Hydration
-
Materials for low cost, scalable, thermochemical hydrogen production S16-325Materials for low cost, scalable, thermochemical hydrogen production
-
Biomimetic Sorbents for CO2 Capture S12-500Biomimetic Sorbents for CO2 Capture