Docket #: S10-055
n-Type Dopants for Organic Electronics
Researchers in Prof. Zhenan Bao's lab at Stanford have developed a series of imidazole derivatives for solution processed, n-type doped organic electronic devices. These air stable, strong n-type dopants effectively improve the conductivity of organic matrix materials, mitigate mobility degradation due to ambient exposure, and improve charge transport. Doping levels can be controlled and modified. Controlled electrical doping increases charge density and reduces ohmic losses in organic devices, resulting in improved film conductivity and increased charge mobility. Most n-type dopants are vacuum deposited with a high activation temperature, making them unsuitable for flexible electronics. The researchers' successful demonstration of air-stable n-channel Organic Thin Film Transistor (OTFT) devices fabricated by vacuum deposition and solution process, opens new opportunities for the development of air-stable n-channel semiconductors. Additional applications include solution-processed organic light-emitting diodes, organic photovoltaics, and n-type doping of carbon nanotube or graphene structures.
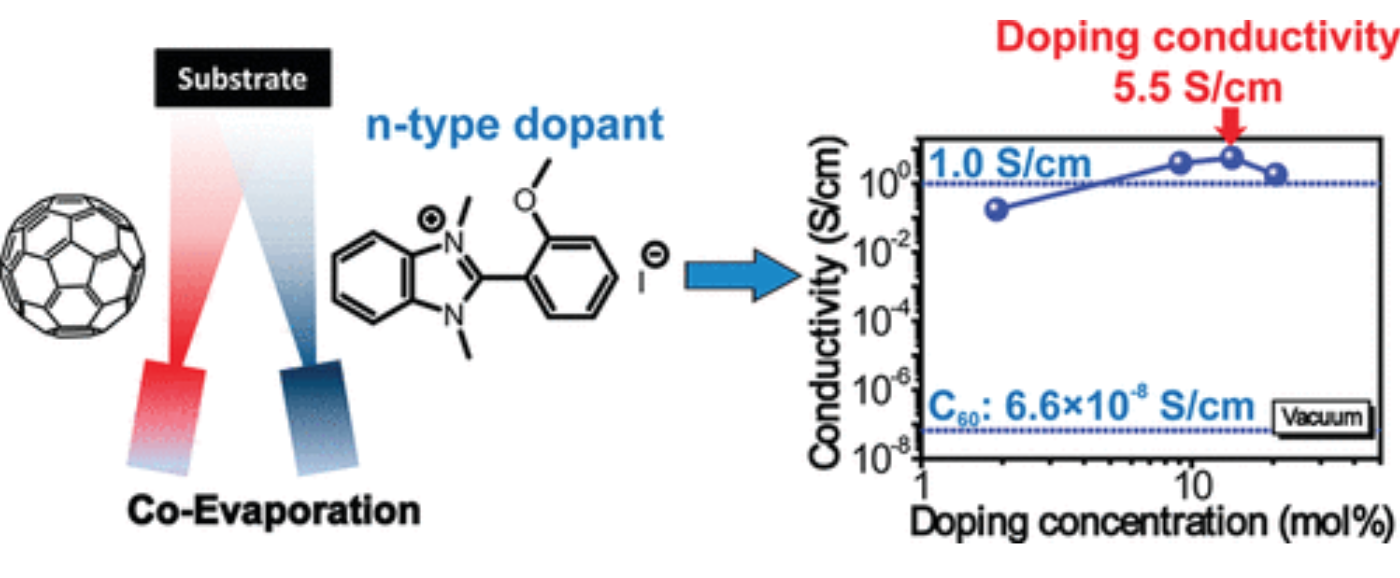
Conductivity of n-Type Dopant
2-(2-Methoxyphenyl)-1,3-dimethyl-1H-benzoimidazol-3-ium Iodide
Image Courtesy the Bao Group
Stage of Development – Prototype
During the development of the patented n-type doped organic electronic device, The Bao Group at Stanford systematically studied doping mechanisms and a variety of imidazole derivatives.
Applications
- Organic electronics, including:
- Organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs)
- Organic thin-film transistors (OTFTs)
- Organic semiconductors (OSCs)
- Organic photovoltaics (OPVs)
Advantages
- Easily synthesized and handled in the industrial production process
- Strong n-type doping effect
- Stable in air
- Fabrication by vacuum deposition and solution process
- Low activation temperature for doping, suitable for solution process and flexible devices
- The doping strength can be controlled and modified by the substitution to make a rational design, such as electron-donor and electron-acceptor groups
Publications
- Wei, P., Menke, T., Naab, B. D., Leo, K., Riede, M., & Bao, Z. (2012). 2-(2-Methoxyphenyl)-1, 3-dimethyl-1 H-benzoimidazol-3-ium iodide as a new air-stable n-type dopant for vacuum-processed organic semiconductor thin films. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 134(9), 3999-4002.
- Wei, P., Oh, J. H., Dong, G., & Bao, Z. (2010). Use of a 1 H-benzoimidazole derivative as an n-type dopant and to enable air-stable solution-processed n-channel organic thin-film transistors. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 132(26), 8852-8853.
- Wei, P., & Bao, Z. (2015).U.S. Patent No. 9,133,130. Washington, DC: U.S. Patent and Trademark Office.
Related Links
Patents
- Published Application: 20110240980
- Published Application: WO2011127075
- Issued: 9,133,130 (USA)
Similar Technologies
-
Method of Organic Semiconductor Thin Film S12-369Method of Organic Semiconductor Thin Film
-
Sorting of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes via Removable Polymer S15-023Sorting of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes via Removable Polymer
-
Solution Sheared Deposition of Organic Semiconductor Thin-Films with Oriented Crystalline Morphology S08-142Solution Sheared Deposition of Organic Semiconductor Thin-Films with Oriented Crystalline Morphology