Docket #: S17-356
PET probes for imaging apoptosis
Stanford researchers at the Rao Lab have developed apoptosis imaging probes with an improved new molecular structure enabling high sensitivity and stability with better performance in vivo.
These probes can image the activity of caspase-3, the executioner enzyme, via a uniquely designed caspase-3-triggered molecular self-assembly process by positron emission tomography (PET).
The early assessment of treatment-induced tumor cell death is of great prognostic value and allows oncologists to timely select the most efficacious treatment using a personalized medicine approach. Since apoptosis is one of the common cell death pathways, there has been strong interest in developing imaging strategies for non-invasive imaging of treatment-induced apoptosis in tumor cells.
Figure
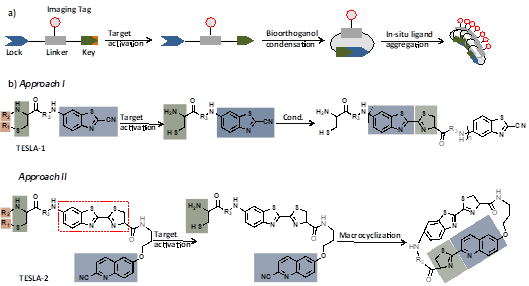
Figure description-a) Illustration of the mechanism of target enabled in-situ ligand aggregation (TESLA); b) approach I through intermolecular bioorthoganol condensation of CBT with cysteine, and approach II via intramolecular cyclization of CHQ with cysteine
Stage of Research
Applications
- Imaging apoptosis:
- Drug research to validate the drug efficacy in subjects non-invasively
- Clinical practice to monitor therapeutic efficacy in cancer patients
Advantages
- Improved imaging probe with new structure, higher sensitivity, better stability
- High specificity for caspase-3
- Non-invasive
- Biocompatible
- Simple to make
- Small size of probe allows:
- Deep tissue penetration
- More extensive biodistribution
- PET probes:
- High tumor/muscle ratio in apoptotic tumors
- High uptake value in apoptotic tumors
- Fluorescent probes:
- Possess NIR spectral properties
- Promotes personalized cancer medicine
- Potential for probe design strategy to be applied to other enzyme targets
Related Links
Patents
- Published Application: 20200085980
- Published Application: 20240042066
- Issued: 11,679,168 (USA)
Similar Technologies
-
Ultra Bright Lanthanide-Doped Nanoparticles for Luminescence Imaging S18-147Ultra Bright Lanthanide-Doped Nanoparticles for Luminescence Imaging
-
ASAP1 and ASAP2: Fluorescent voltage sensor with fast kinetics for imaging high-frequency neuronal electrical activity S13-389ASAP1 and ASAP2: Fluorescent voltage sensor with fast kinetics for imaging high-frequency neuronal electrical activity
-
Fluorescent saccharide sensors for early detection of gastrointestinal diseases S17-396Fluorescent saccharide sensors for early detection of gastrointestinal diseases