Docket #: S23-282
Robust 3D printed pyrolytic carbon micro-array patch for transdermal applications
Researchers at Stanford have combined 3D printing and pyrolysis to produce a robust and biocompatible high resolution micro-array patch (MAP) for transdermal drug delivery.
MAPs are an innovative transdermal drug delivery system that allows for relatively painless, efficient, and controlled administration of medications through the skin. They are composed of an adhesive backing and an array of drug-eluting microneedles. Additive manufacturing, commonly known as 3D printing, is emerging as the preferred fabrication method for MAPs because it offers more design options and capabilities compared to the conventional silicon microfabrication method. However, the materials currently used to 3D print MAPs have limited printing resolution, are often too soft for complete insertion into the skin, and lose biocompatibility with wear.
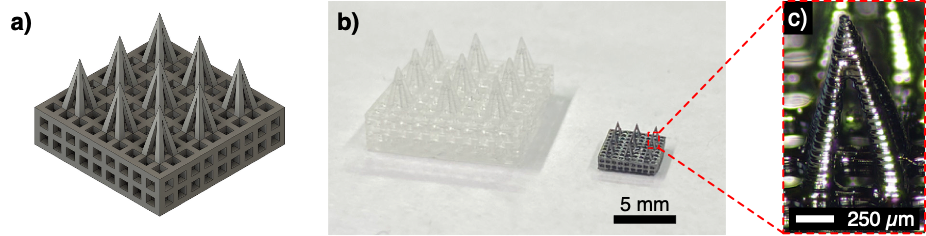
To overcome these limitations, Stanford researchers used a pyrolytic polymer to manufacture MAPs. They 3D printed the desired micro-array structure using a soft pyrolytic polymer. The printed structure was then subjected to pyrolysis, a thermal decomposition process, to form a miniaturized replica made of hard monolithic carbon. These steps ensured both high-resolution structural details and enhanced mechanical strength and stability, facilitating skin insertion and drug release. Additionally, high electrical conductivity of these MAPs enabled their use in electrochemical sensing.
Figure:
Stage of Development
Prototype
Applications
- Drug delivery/transfection, electrochemical sensing:
- Point-of-care
- Rapid response to pandemic events
- Self-administration
Advantages
- High resolution
- Biocompatible
- Robust
- Design flexibility
- Scalable
- Low electrical resistance – biomarker detection
Publications
- Rajesh, N. U., Coates, I., et al. (2022). 3D-Printed Microarray Patches for Transdermal Applications. JACS Au, 2(11), 2426–2445.
Related Links
Similar Technologies
-
An Extrudable Biomaterial with Heat-Resistant Bioactivity and Tunable Degradation S23-458An Extrudable Biomaterial with Heat-Resistant Bioactivity and Tunable Degradation
-
Drug-imprinted hydrogel for controlled-release wound healing therapy with FAK inhibitors S14-447Drug-imprinted hydrogel for controlled-release wound healing therapy with FAK inhibitors
-
Use of recombinant osteopontin (SPP1) protein for prevention of foreign body response S23-249Use of recombinant osteopontin (SPP1) protein for prevention of foreign body response