Docket #: S22-403
Solving brain circuit function and dysfunction with computational modeling and optogenetic fMRI
Stanford researchers at the Lee Lab have developed a method to understand whole-brain circuit mechanisms underlying neurological disease and its application to predict the outcome of therapeutic interventions.
By combining optogenetic fMRI with computational modeling, cell type-specific, large-scale brain circuit function and dysfunction are now starting to be quantitatively parameterized. These new findings can pave the path for future therapeutics developments based on a systems engineering approach aimed at directly restoring brain function.
Figure:
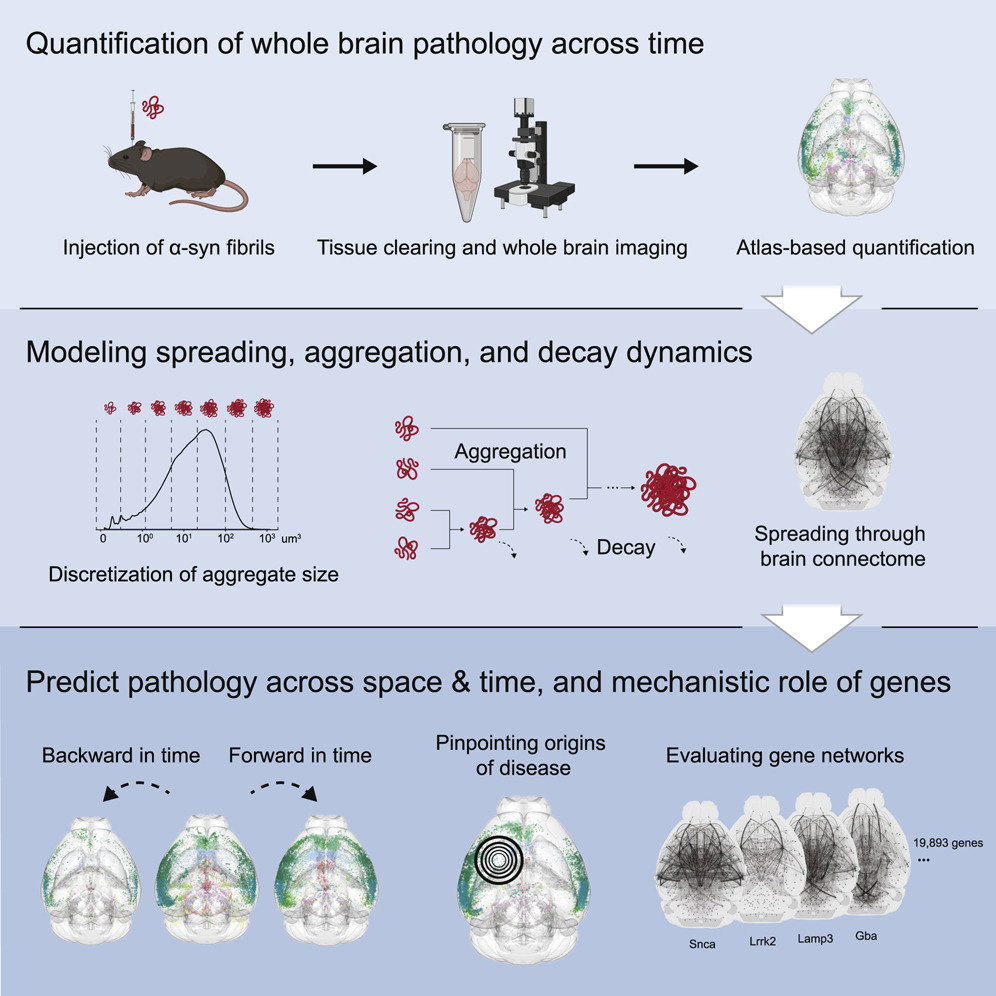
Figure description: Graphical Abstract
Image credit: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2022.111631
Stage of Development
Applications
- Neuromodulation therapy design for neurogenerative diseases
- The method can be applied to predict the optimal targets and parameters of the neuromodulation treatments for a number of neurological disorders, including but not limited to Parkinsons disease (PD), dystonia, and epilepsy
Advantages
- Systematically designed treatments for brain disorders
- Enables virtual neuromodulations for the treatments of neurological disorders
- By implementing such virtual neuromodulations, rapid optimization and customization can be achieved that saves the time and financial costs of carrying out in vivo experiments
- Incorporates cell-type information to modeling
Publications
- Lee, Jin Hyung, Qin Liu, and Ehsan Dadgar-Kiani. "Solving brain circuit function and dysfunction with computational modeling and optogenetic fMRI." Science 378, no. 6619 (2022): 493-499.
- Dadgar-Kiani, Ehsan, Gregor Bieri, Ronald Melki, Aaron D. Gitler, and Jin Hyung Lee. "Mesoscale connections and gene expression empower whole-brain modeling of ?-synuclein spread, aggregation, and decay dynamics." Cell Reports 41, no. 6 (2022): 111631.
Related Links
Patents
- Published Application: WO2024073593
- Published Application: 20250325707
Similar Technologies
-
Neuro-navigation device for localization of internal anatomical regions S17-412Neuro-navigation device for localization of internal anatomical regions
-
Pathology modifying neuromodulation therapy design S22-398Pathology modifying neuromodulation therapy design
-
Selective modulation of anxiety features S13-095Selective modulation of anxiety features