Docket #: S22-398
Pathology modifying neuromodulation therapy design
Stanford researchers at the Lee Lab have developed a new system and method for measuring pathology then applying a novel algorithm to optimize neurostimulation therapy for altering pathology for treatment of neurodegenerative diseases.
Optimal neurostimulation therapy parameters include the location, strength, and frequency of neurostimulation. For example, the location of neurostimulation can be set based on where this algorithm predicts pathology to occur. Other parameters such as stimulation frequency and pulse width can subsequently be set to target specific neuronal cell- types or circuits within the brain.
This model empowers mechanistic understanding and accurate prediction of disease progression, paving the way for the development and testing of therapeutic interventions.
Application of this new strategy is described in Stanford docket S22-403 "Solving brain circuit function and dysfunction with computational modeling and optogenetic fMRI"
Figure:
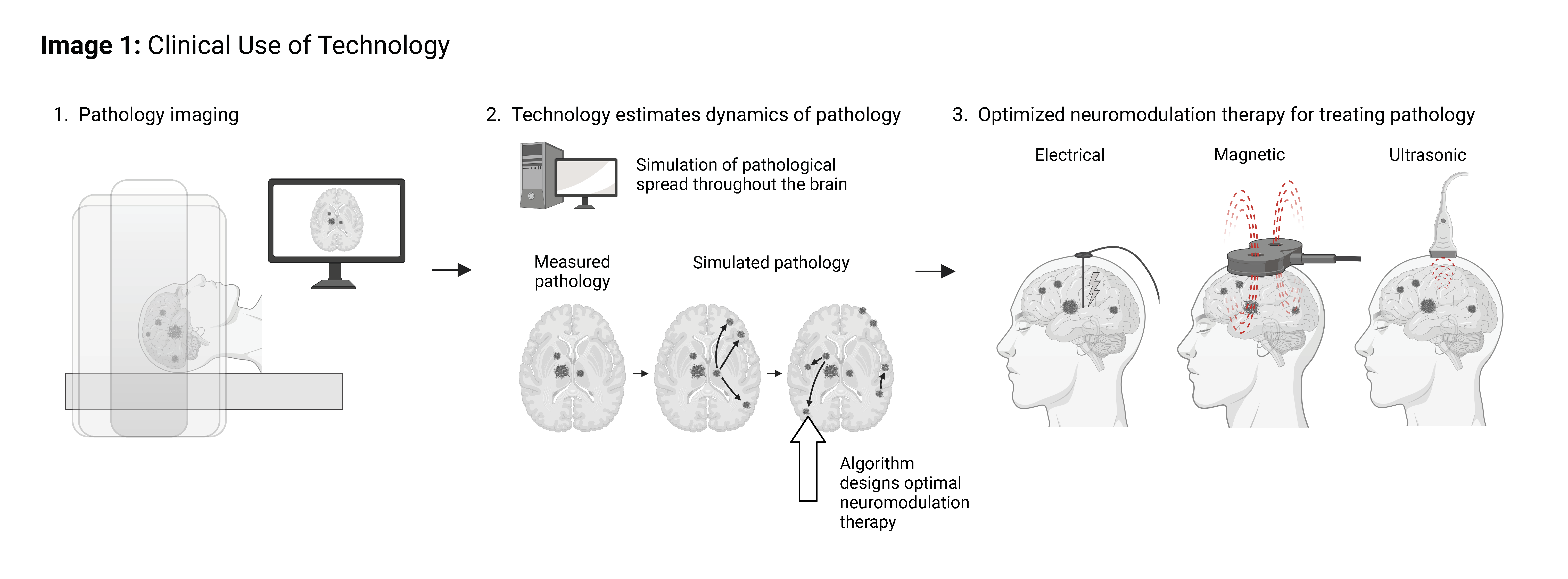
Figure description: Clinical Use of Technology
Image credit: Lee Lab
Stage of Development
Applications
- Neurostimulation therapy based on cell-type and brain circuit targeting
- Commercial application is to read brain's pathology via imaging and apply an algorithm to predict pathology, optimizing design of therapy
Advantages
- Uses measured pathology to design the optimal neuromodulation parameters
- pathological state used for targeted neuromodulation therapy
- as compared to pharmaceutical methods
- Can be applied to any neurostimulation method- Optogenetic, Acoustic, Magnetic, or Electrical (i.e., Deep Brain Stimulation)
Publications
- Lee, Jin Hyung, Qin Liu, and Ehsan Dadgar-Kiani. "Solving brain circuit function and dysfunction with computational modeling and optogenetic fMRI." Science 378, no. 6619 (2022): 493-499.
- Dadgar-Kiani, Ehsan, Gregor Bieri, Ronald Melki, Aaron D. Gitler, and Jin Hyung Lee. "Mesoscale connections and gene expression empower whole-brain modeling of ?-synuclein spread, aggregation, and decay dynamics." Cell Reports 41, no. 6 (2022): 111631.
Related Links
Patents
- Published Application: WO2024073597
- Published Application: 20250342933
Similar Technologies
-
Neuro-navigation device for localization of internal anatomical regions S17-412Neuro-navigation device for localization of internal anatomical regions
-
Solving brain circuit function and dysfunction with computational modeling and optogenetic fMRI S22-403Solving brain circuit function and dysfunction with computational modeling and optogenetic fMRI
-
A wirelessly powered, fully internal implant that enables optogenetic stimulation of brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nervous system in untethered mice S14-453A wirelessly powered, fully internal implant that enables optogenetic stimulation of brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nervous system in untethered mice