Docket #: S23-004
Spectral routers for snapshot multispectral imaging
Stanford researchers working as part of the E. L. Ginzton Laboratory, an interdisclplinary research lab for applied physics, have developed a new device, called a spectral router, which can separate light into spectral components without loss of photons in a (sub)wavelength size footprint. This spectral router enables single-chip snapshot spectral imaging sensors and systems that are highly (up to ~100%) photon efficient to provide spectral information without sacrificing spatial information. A spectral router in a single-chip snapshot imaging system with N spectral channels can improve photon efficiency N-fold, in a much smaller footprint, compared to a conventional multispectral filter array. While spectral routers benefit all spectral imaging applications, this extremely compact and photon efficient solution can also further increase multispectral imaging use cases by enabling photon-efficient, high-spatial resolution systems on highly portable platforms (e.g., smart phones, tablets).
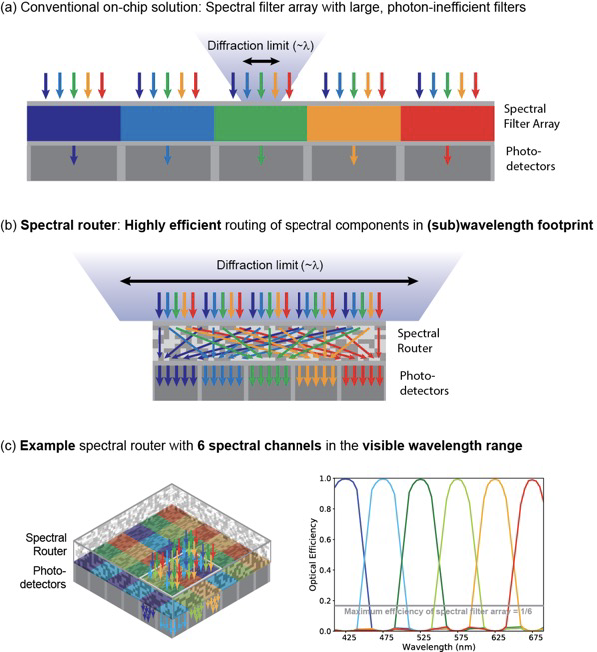
Figure Description:(a) Conventional on-chip solution for single-chip spectral imaging systems based on spectral filter array with photon-inefficient spectral filters which are larger than the wavelength and thus limit the spatial resolution of the captured image, (b) Spectral router providing highly efficient routing of spectral components in a (sub)wavelength footprint without sacrificing spatial resolution in the image, (c) Example spectral router with 6 spectral channels, in a 2 by 3 channel layout, in the visible wavelength range. The optical efficiency of the router can be ideal (~100%) for the 6 channels with negligible (~0%) crosstalk between channels. For comparison, the gray line in the graph shows the maximum theoretical efficiency (=1/6) of a spectral filter array.
Stage of Development
Applications
- Spectral imaging and imaging spectroscopy applications including but not limited to: Bio-medical imaging, microscopy, precision agriculture, food inspection, machine vision, forensics and counterfeit detection
- Single-chip spectral imaging systems based on solid state image sensors and (infrared) focal plane arrays, CMOS image sensors, CCD image sensors that can be used in smartphone cameras, security cameras, and automotive cameras
Advantages
- High (~100%) photon efficiency across spectral channels
- Negligible (~0%) crosstalk between spectral channels
- Extremely compact (sub)wavelength size to allow spectral imaging without sacrificing spatial resolution at the image plane
- Flexible design (spectral shapes, number of channels, channel separations, …)
- Can operate in many spectral ranges (visible, infrared, …)
- Standard semiconductor nanolithography processing, including CMOS Image Sensor (CIS) processing
Publications
- Spectral router for the short-wave infrared wavelength range:
- Catrysse, Peter B., and Shanhui Fan. "Multispectral Routers for Snapshot Spectral Imaging." In CLEO: Applications and Technology, pp. ATu3K-5. Optica Publishing Group, 2023.
- Spectral router for the visible wavelength range:
- Catrysse, Peter B., and Shanhui Fan. "Spectral Routers for Snapshot Imaging." In Imaging Systems and Applications, pp. IM4E.3. Optica Publishing Group, 2023.
Related Links
Patents
- Published Application: WO2025151129
Similar Technologies
-
Eliminating Crosstalk by Rearranging Patterned Thin-Film Filters on Image Sensor S22-135Eliminating Crosstalk by Rearranging Patterned Thin-Film Filters on Image Sensor
-
Photon spin processor for on-chip classical and quantum information systems S24-212Photon spin processor for on-chip classical and quantum information systems
-
Efficient wide-field nanosecond imaging methods using Pockels cells for low-light applications S18-388Efficient wide-field nanosecond imaging methods using Pockels cells for low-light applications