Docket #: S17-198
Stable Interface for Lithium Batteries via Stitching Two-Dimensional Atomic Crystals by Atomic Layer Deposition
Stanford researchers at the Yi Cui Lab have demonstrated a new method to increase stability of lithium battery interfaces via stitching of two-dimensional atomic crystals by atomic layer deposition (ALD) which provides an innovative way to prepare chemically and mechanically stable hybrid film. This hybrid LiF/h-BN film successfully suppresses lithium dendrite formation during both the initial electrochemical deposition onto a copper foil and the subsequent cycling. The protected lithium electrodes exhibit good cycling behavior with more than 300 cycles at relatively high coulombic efficiency (>95%) in an additive-free carbonate electrolyte.
Figure
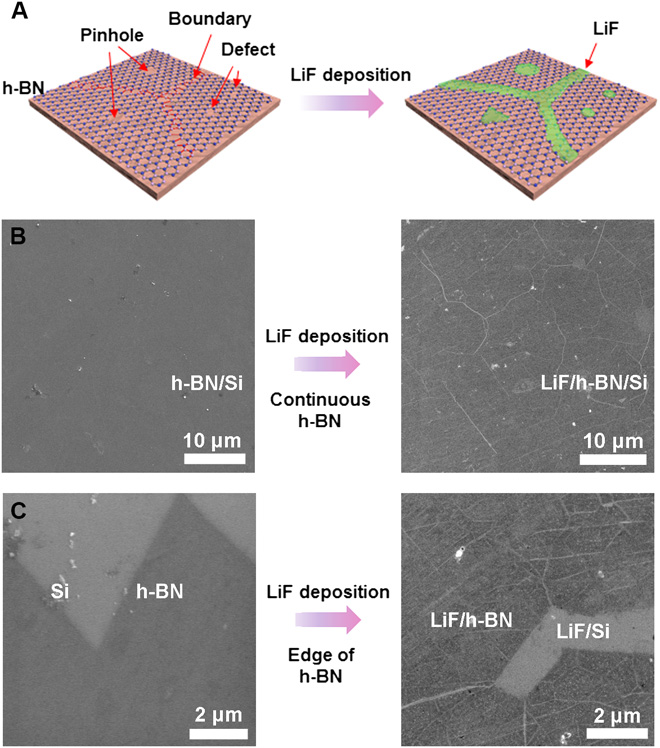
Figure description - SEM characterization
(A) Schematics of selective ALD LiF deposition on h-BN. (B) SEM characterization of 50 cycles of ALD LiF deposition on continuous h-BN. (C) SEM characterization of 50 cycles of ALD LiF deposition on the edge of h-BN.
Stage of Research
Applications
- Lithium batteries to reduce side reactions in between electrolyte and electrode
Advantages
- Innovative method to increase stability of lithium battery interfaces
- Suppresses lithium dendrite formation
- Improves safety of batteries
- Improves the Coulombic efficiencies of batteries
- Prolongs the cycle life of batteries
- Interfacial layer is extremely thin
- Adoption of interfacial layer does not compromise the overall energy density of the battery
- Expandable to other metal anodes or electrochemical metal plating
- Provides a promising route to commercialization of lithium metal anode based batteries
Publications
- Xie, J., Liao, L., Gong, Y., Li, Y., Shi, F., Pei, A., Sun, J., Zhang, R., Kong, B., Subbaraman, R. and Christensen, J., 2017. Stitching h-BN by atomic layer deposition of LiF as a stable interface for lithium metal anode. Science advances, 3(11), p.eaao3170.
Related Links
Patents
- Published Application: 20200131638
- Issued: 11,499,228 (USA)
Similar Technologies
-
Highly Conducting Solid Electrolytes for Batteries S15-203Highly Conducting Solid Electrolytes for Batteries
-
Nanoscale Interfacial Engineering with Interconnected Hollow Carbon Nanospheres for Stable Lithium Metal Anode S14-006Nanoscale Interfacial Engineering with Interconnected Hollow Carbon Nanospheres for Stable Lithium Metal Anode
-
Coating Design based on Ion-conductive Organic Networks (IONs) to improve safety and stability of Lithium Metal Batteries S18-311Coating Design based on Ion-conductive Organic Networks (IONs) to improve safety and stability of Lithium Metal Batteries