Docket #: S12-107
Strong and stable doping of carbon nanotubes and graphene by MoOx for transparent electrodes
Stanford researchers have developed and tested a new method of stably and strongly doping CNTs and graphene using MoOx as a nontoxic, inexpensive, vacuum or solution deposited alternative to strong liquid acids. Carbon nanotube (CNT) networks and graphene thin films have recently been studied intensively for transparent electrodes which are crucial for touch screen, flat panel display and solar cell technologies. Excellent thermal and chemical stability coupled with high conductivity makes MoOx-CNT composites extremely attractive candidates for practical transparent electrodes.
Figure
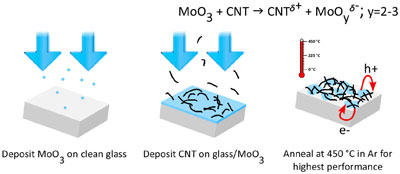
Figure description - Schematic showing the fabrication of MoOx-CNT transparent conductors.
Stage of Research
Applications
- Transparent electrodes for:
- thin film solar cells
- flat panel displays
- touch screens
Advantages
- Thermal and chemical stability coupled with high conductivity
- Can be deposited by either thermal evaporation or from solution-based precursors;
- Flexible and stretchable
- Solution processability
- Mild, stable, reliable, low toxicity doping method
Publications
- U.S. Patent Application No. 13/911,848
- Sondra L. Hellstrom, Michael Vosgueritchian, Randall M. Stoltenberg, Irfan Irfan, Mallory Hammock, Yinchao Bril Wang, Chuancheng Jia, Xuefeng Guo, Yongli Gao‡, and Zhenan Bao, Strong and Stable Doping of Carbon Nanotubes and Graphene by MoOx for Transparent Electrodes, Nano Lett. 2012 12(7), pp.3574-3580, published online June 13, 2012. DOI: 10.1021/nl301207e
Related Links
Patents
- Published Application: 20130330559
Similar Technologies
-
Nanofiber Transparent Electrodes S09-418Nanofiber Transparent Electrodes
-
Broadband, polarization-independent, omnidirectional, metamaterial-based antireflection coating for solar cells S16-418Broadband, polarization-independent, omnidirectional, metamaterial-based antireflection coating for solar cells
-
Low-Temperature Synthesis of Polycrystalline Semiconductor Thin Films on Amorphous Substrates S10-129Low-Temperature Synthesis of Polycrystalline Semiconductor Thin Films on Amorphous Substrates