Docket #: S17-280
Ultrasound Imaging with Spectral Compounding for Speckle Reduction
Stanford researchers at the Steven Chu Lab have developed and patented a method and apparatus to optimize speckle suppression in ultrasound imaging, usable for diagnostic purposes. This method uses Fourier-transform limited pulses for spectral compounding. The optimization of pulse shape allows for the optimization of the trade-off between speckle reduction and axial resolution. Compared to images without spectral compounding, this invention can reduce the speckle noise by 2-3X and dramatically improve image quality, as demonstrated in preliminary data.
Figure
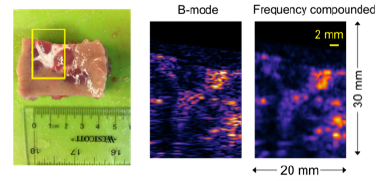
Figure description - Use of Fourier-filter speckle reduction method to image a piece of porcine kidney. Figure shows optical image (left panel) of a portion of kidney tissue imaged by ultrasound. The minor and major calyces appear white in the optical image. The same features can be identified in the conventional B-mode image (middle panel). The frequency compounded image shows reduced speckle while maintaining good spatial resolution.
Stage of Development - Proof of Concept
Applications
- Diagnostic Ultrasound Imaging
Advantages
- Method minimizes speckle for given spatial resolution
- Improves image quality
- Enables general diagnostic purposes
Publications
- Li, Y., & Chu, S. (2021). U.S. Patent No. 10,905,401. Washington, DC: U.S. Patent and Trademark Office.
- Li, Y., Winetraub, Y., Liba, O., de la Zerda, A., & Chu, S. (2018). Optimization of the trade-off between speckle reduction and axial resolution in frequency compounding. IEEE transactions on medical imaging, 38(1), 107-112. DOI: 10.1109/TMI.2018.2856857
Related Links
Patents
- Published Application: 20190008485
- Published Application: WO2019014070
- Published Application: 20210251612
- Issued: 10,905,401 (USA)
Similar Technologies
-
Non-linear contrast for high resolution ultrasound imaging S17-395Non-linear contrast for high resolution ultrasound imaging
-
Thermoacoustic imaging for handheld medical diagnostic and security screening applications S14-053Thermoacoustic imaging for handheld medical diagnostic and security screening applications
-
System and device for improved ultrasound cavitation mapping S17-138System and device for improved ultrasound cavitation mapping