Docket #: S12-036
CLARITY: Transparent Tissue for 3D Imaging of Neuronal Networks and Subcellular Structures
Researchers in Prof. Karl Deisseroth's laboratory have patented a revolutionary technique that can be utilized to map neural circuits in the whole brain. This technology, called CLARITY (Clear, Lipid-exchanged, Anatomically Rigid, Imaging/immunostaining compatible, Tissue hYdrogel), employs a hydrogel that preserves proteins, small peptides, small molecules, and nucleic acids in their three-dimensional distribution as found in original tissue. Following a clearing procedure, CLARITY renders tissue ultrastructures highly transparent and permeable to macromolecules, enabling visualization of both three-dimensional structure and fine molecular details of intact whole tissues without mechanical sectioning. Compared to the current Scale technology, this process is much faster (2 days vs. 5 weeks) and more effective removing opaque molecules.
Immunostaining the now transparent tissue can reveal subcellular structures in their native three-dimensional context. The same tissue can then be washed and stained again for subsequent analyses. CLARITY has a wide range of applications such as high-throughput mapping and analysis of neuronal networks, mapping cellular components in whole organisms, or clinical histology of biopsies and post mortem tissue.
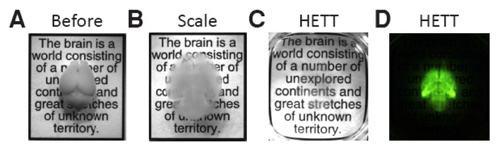
Images courtesy the Deisseroth Lab
CLARITY imaging of the whole intact mouse brain. Photographs of whole mouse brains (4 months old). (A) Before clearing (B) Cleared by the Scale method for 5 weeks (C) Cleared by the CLARITY method for two days (D) Fluorescent image of the same brain shown in C.
Stage of Development
Deisseroth Lab researchers regularly use CLARITY in their neural physiology research and actively maintain the CLARITY resource center.
Applications
- Research:
- 3-dimensional mapping of complex neural circuits with cellular resolution
- research tool for BRAIN initiative to map the human brain
- probing and mapping neural networks and other cellular components in the context of intact tissue or organisms
- storing, rendering, and using, and eventually actuating, the full connectivity of a human brain post mortem
- obtaining 3D structural information from clinical biopsies such as heart, kidneys, tumors and other tissues
Advantages
- Whole tissue analysis — no sectioning
- faster and less laborious than mechanical sectioning
- compatible with immunostaining or molecular phenotyping that is not possible with optical sectioning
Publications
- Deisseroth, K. A., & Chung, K. (2021). U.S. Patent Application No. 16/950,640.
- Deisseroth, K. A., & Chung, K. (2020). U.S. Patent No. 10,545,075. Washington, DC: U.S. Patent and Trademark Office.
- Hsueh, B., Burns, V. M., Pauerstein, P., Holzem, K., Ye, L., Engberg, K., ... & Deisseroth, K. (2017). "Pathways to clinical CLARITY: volumetric analysis of irregular, soft, and heterogeneous tissues in development and disease." Scientific reports, 7(1), 1-16.
- Chung, K., Wallace, J., Kim, S. Y., Kalyanasundaram, S., Andalman, A. S., Davidson, T. J., ... & Deisseroth, K. (2013). Structural and molecular interrogation of intact biological systems. Nature, 497(7449), 332-337. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12107
- New York Times — Brains as Clear as Jell-O for Scientists to Explore
- Scientific American — Interview with Prof. Deisseroth
- Nature — See-through brains clarify connections
- The Verge — Technique to create transparent brains could transform neuroscience
- Inside Stanford Medicine — Getting CLARITY
- Stanford News — President Obama's new $100 million brain research initiative taps several Stanford scientists
Video
Related Links
Patents
- Published Application: WO2014025392
- Published Application: 20150144490
- Published Application: 20170219465
- Published Application: 20210215581
- Issued: 10,545,075 (USA)
Similar Technologies
-
Efficient wide-field nanosecond imaging methods using Pockels cells for low-light applications S18-388Efficient wide-field nanosecond imaging methods using Pockels cells for low-light applications
-
Light sheet fluorescence microscopy using high speed structured and pivoting illumination S16-332Light sheet fluorescence microscopy using high speed structured and pivoting illumination
-
RNA fixation and detection in CLARITY-based hydrogel tissue S15-424RNA fixation and detection in CLARITY-based hydrogel tissue