Docket #: S16-240
Electro-thermochemical Li Cycling for NH3 Synthesis from N2 and H2O
Stanford researchers at the Jaramillo, Nørskov, and Cargnello Labs have developed an improved system to generate NH3 (ammonia) from N2 and H2O via a low-pressure, electro-thermochemical, sustainable alternative to the conventional Haber-Bosch process.
The prevalent Haber-Bosch manufacturing technique, which reacts N2 with H2, has a number of drawbacks. It consumes large amounts of natural gas to obtain H2, emits carbon dioxide, and requires high-pressure conditions that force the use of expensive centralized factories. The new technology resolves a number of these concerns. The use of water in place of H2 obviates the need for fossil fuels, the technique emits only H2O and O2 as byproducts, and less rigorous pressure requirements reduce the cost of running the process. Moreover, this technique could allow for the local production of ammonia that would then be put immediately into the soil, reducing the cost of fertilizer and maximizing nitrogen utilization efficiency. Thus, this technology could allow for cheaper, less energy-consuming, and more environmentally friendly production and use of ammonia, compared to current standards.
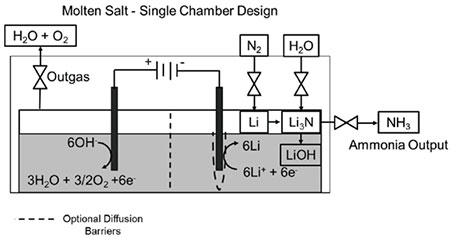
Figure description - A schematic of one possible set-up for an ammonia-producing system; given N2 and H2O inputs, the system releases ammonia and byproducts H2O and O2.
Stage of Research as of October 2016
Applications
- Ammonia production from water and N2 for use as:
- Fertilizer
- Chemical precursor to many nitrogen-containing chemicals
- Fuel alternative
- Energy storage from renewable sources (wind, solar, etc.)
Advantages
- Ammonia production without the use of H2 and fossil fuels
- Energy-efficient May provide a means by which to resolve energy concerns with the Haber-Bosch process, which requires over 1% of the entire global energy and 3-5 % of the natural gas supply for pre-requisite hydrogen production
- Lower-cost less high-pressure requirements than Haber-Bosch, allowing for less equipment and operational costs
- Enables local manufacturing- could be produced locally instead of inside large factories, reducing distribution costs and maximizing nitrogen utilization efficiency
- Environmentally-friendly: unlike Haber-Bosch, does not emit CO2
Publications
- J.M. McEnaney, A.R. Singh, J.A. Schwalbe, J. Kibsgaard, J.C. Lin, M. Cargnello, T.F. Jaramillo, and J.K. Nørskov, "Ammonia synthesis from N2 and H2O using a lithium cycling electrification strategy at atmospheric pressure". Energy and Environmental Science; Issue 7, 2017.
Related Links
Similar Technologies
-
Oxygen tolerant hydrogenases by mutating electron supply pathway S15-300Oxygen tolerant hydrogenases by mutating electron supply pathway
-
Low Cost, Bifunctional Electrocatalyst for Water Splitting S14-465Low Cost, Bifunctional Electrocatalyst for Water Splitting
-
High efficiency electrocatalysis with lung-inspired architecture S17-342High efficiency electrocatalysis with lung-inspired architecture