Docket #: S17-114
Fully Water-Soluble, Fluorescence-Based, Synthetic Small-Molecule Hydrazine Sensor for Liquid Analysis
Stanford researchers have invented a fully water-soluble, orange hydrazine sensor that can robustly quantify the toxin hydrazine in liquids such as drinking water, waste water (treated and untreated), and bodily fluids. The sensor turns colorless upon exposure to hydrazine in water; the resulting colorless dye brightly fluoresces green when exposed to UV light.
Superior to many existing sensors, water solubility is a new feature of this sensor that allows an entire sample to be easily mixed for enhanced sensing sensitivity and reliability. The water solubility and spectral properties of this dye make the sensor ideal for hydrazine level assessment in aqueous samples.
Figure
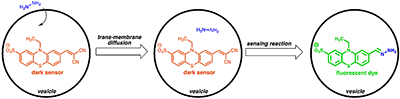
Figure description - Invention of Water-Soluble Alternative: SPT
Stage of Research
Applications
- Drinking water safety assessment
- Environmental water assessment
- Waste water treatment
- Urinalysis
- Basic science research (e.g. hydrazine production/diffusion experiments)
Advantages
- Full water solubility enables:
- Higher amounts of dye for faster sensing
- More consistent results
- Ease of dispersion if analyzing large sample
- Faster sensing
- Easy method to detect presence of hydrazine
- Straightforward to synthesize
Publications
- Frank R. Moss III, Steven R. Shuken, Jaron A. M. Mercer, Carolyn M. Cohen, Thomas M. Weiss, Steven G. Boxer, and Noah Z. Burns, "Ladderane phospholipids form a densely packed membrane with normal hydrazine and anomalously low proton/hydroxide permeability," PNAS September 11, 2018 115 (37) 9098-9103; published ahead of print August 27, 2018.
Related Links
Patents
- Published Application: 20190033215
- Issued: 10,732,108 (USA)
Similar Technologies
-
Using Raman spectroscopy and machine learning for rapid, label-free bacterial detection in wastewater S24-426Using Raman spectroscopy and machine learning for rapid, label-free bacterial detection in wastewater
-
Ultratrace and Multiplex Visual/Smartphone Detection of Heavy Metal Ions by their Sulfidation on a Superhydrophobic Concentrator S20-002Ultratrace and Multiplex Visual/Smartphone Detection of Heavy Metal Ions by their Sulfidation on a Superhydrophobic Concentrator
-
Flexible electrochemical stripping to recover alkaline and acidic ammonia from wastewaters S20-349Flexible electrochemical stripping to recover alkaline and acidic ammonia from wastewaters